AutoCAD Student: Embark on a journey into the world of computer-aided design (CAD) with AutoCAD, the industry-leading software used by professionals across various fields. Whether you’re an aspiring architect, engineer, or designer, AutoCAD provides a powerful platform to bring your ideas to life.
Table of Contents
This comprehensive guide will equip you with the essential knowledge and skills to navigate the AutoCAD interface, master drawing techniques, and create both intricate 2D designs and complex 3D models. From understanding fundamental concepts to exploring advanced features, this guide will empower you to confidently tackle your design projects.
Introduction to AutoCAD for Students
AutoCAD is a powerful and widely used computer-aided design (CAD) software that allows users to create, edit, and share 2D and 3D designs. It is an essential tool for professionals in various fields, including architecture, engineering, construction, and manufacturing. This introduction will provide you with a comprehensive overview of AutoCAD, covering its history, purpose, applications, and versions specifically tailored for students.
History and Purpose of AutoCAD
AutoCAD was first released in 1982 by Autodesk, revolutionizing the design process by transitioning from manual drafting to digital design. It quickly gained popularity due to its user-friendly interface, powerful features, and ability to create precise and detailed drawings. Today, AutoCAD remains the industry standard for CAD software, used by millions of professionals worldwide. Its primary purpose is to enable users to create accurate and professional drawings, plans, and models, enhancing efficiency and collaboration in design projects.
Applications of AutoCAD
AutoCAD’s versatility makes it applicable across a wide range of fields, including:
- Architecture: Creating architectural floor plans, elevations, sections, and 3D models of buildings.
- Engineering: Designing mechanical parts, electrical circuits, and structural components.
- Construction: Developing construction drawings, site plans, and building information models (BIM).
- Manufacturing: Creating detailed drawings of products, assemblies, and tooling.
- Civil Engineering: Designing roads, bridges, and other infrastructure projects.
- Landscape Architecture: Creating site plans, landscape designs, and irrigation systems.
Versions of AutoCAD for Students
Autodesk offers various versions of AutoCAD tailored for different needs and budgets. For students, the most popular options are:
- AutoCAD LT: A more affordable version with essential 2D drafting features, ideal for beginners.
- AutoCAD: The full version with advanced features for both 2D and 3D design, providing greater flexibility and capabilities.
- Autodesk Fusion 360: A cloud-based CAD/CAM/CAE software that integrates design, engineering, and manufacturing processes, offering a comprehensive solution for students.
Each version offers unique features and benefits, making it crucial to choose the one that best suits your learning objectives and project requirements.
Downloading, Installing, and Activating AutoCAD
Autodesk provides a straightforward process for downloading, installing, and activating AutoCAD for educational purposes.
- Visit the Autodesk Education Community website: This platform offers access to educational software licenses and resources. You may need to create an account or log in using your school credentials.
- Locate the AutoCAD download link: Browse the website for the specific version of AutoCAD you need (AutoCAD LT, AutoCAD, or Fusion 360). Click on the download link to initiate the download process.
- Run the installer: Once the download is complete, run the installer file and follow the on-screen instructions. You may need to provide your student ID or other relevant information for verification.
- Activate your software: After installation, you’ll need to activate your AutoCAD software using the provided license information. This typically involves entering a product key or accessing a web-based activation tool.
Following these steps will ensure you have successfully downloaded, installed, and activated AutoCAD for your educational use.
AutoCAD Interface and Tools
The AutoCAD interface provides a comprehensive workspace for creating and manipulating 2D and 3D drawings. It features a user-friendly layout with several key components that facilitate efficient design and drafting. Understanding these components is crucial for effectively utilizing AutoCAD’s capabilities.
The AutoCAD Interface Layout
The AutoCAD interface consists of several key components that work together to provide a comprehensive workspace for design and drafting.
- Main Toolbar: Located at the top of the screen, the main toolbar provides quick access to frequently used commands, such as New, Open, Save, and Print. It also includes tools for navigating the drawing area, zooming, and panning.
- Ribbon: The ribbon is a collection of tabs and panels that organize the various tools and commands available in AutoCAD. Each tab corresponds to a specific function, such as drawing, editing, annotation, and visualization. Within each tab, panels contain related tools and options.
- Command Line: The command line, located at the bottom of the screen, provides a text-based interface for entering commands and viewing system messages. It allows users to execute commands directly by typing them in, offering a more precise and efficient way to interact with AutoCAD.
- Drawing Area: The drawing area is the central workspace where you create and edit your designs. It’s a digital canvas where you can draw, modify, and manipulate objects.
- Status Bar: The status bar, located at the bottom of the screen, provides information about the current drawing, such as the coordinates of the cursor, the snap settings, and the current layer.
Drawing Tools
Drawing tools are essential for creating the fundamental elements of your designs. AutoCAD offers a comprehensive set of tools for creating various geometric shapes, lines, and curves.
- Line Tool: The Line tool creates straight lines by defining two points. You can use the Line tool to draw individual lines or to create connected lines that form complex shapes.
- Arc Tool: The Arc tool creates curved segments, defined by three points: the start point, the center point, and the end point. Arcs are essential for creating curved shapes, circles, and other complex geometries.
- Circle Tool: The Circle tool creates circles by defining a center point and a radius. You can use the Circle tool to create circles of various sizes and to incorporate them into your designs.
- Rectangle Tool: The Rectangle tool creates rectangles by defining two opposite corners. You can use the Rectangle tool to create rectangular shapes, including squares.
- Polyline Tool: The Polyline tool creates a series of connected line segments that can be straight or curved. It’s a versatile tool for creating complex shapes and Artikels.
- Spline Tool: The Spline tool creates smooth curves that pass through a series of defined points. Splines are useful for creating organic shapes and curves.
Editing Tools
Once you have created your drawing elements, editing tools allow you to modify and refine your design. These tools enable you to adjust shapes, sizes, positions, and other properties of your objects.
- Move Tool: The Move tool allows you to relocate objects within your drawing. You can move individual objects or groups of objects to different positions.
- Copy Tool: The Copy tool creates duplicates of selected objects. This tool is useful for replicating objects, creating patterns, or adding symmetry to your design.
- Rotate Tool: The Rotate tool allows you to rotate objects around a specified pivot point. You can use the Rotate tool to adjust the orientation of objects or to create symmetrical designs.
- Scale Tool: The Scale tool allows you to resize objects proportionally. You can enlarge or shrink objects while maintaining their original proportions.
- Trim Tool: The Trim tool allows you to remove portions of objects that extend beyond other objects. This tool is useful for creating clean intersections and eliminating unwanted lines.
- Extend Tool: The Extend tool allows you to extend the length of objects to meet other objects. This tool is useful for creating seamless connections and eliminating gaps between objects.
Dimensioning Tools
Dimensioning tools are crucial for providing accurate measurements and annotations to your drawings. They allow you to add dimensions, notes, and other annotations to communicate the size, shape, and other properties of your design.
- Linear Dimension Tool: The Linear Dimension tool creates straight lines with arrows at both ends, indicating the distance between two points. It’s used to measure the length of lines and other straight segments.
- Radial Dimension Tool: The Radial Dimension tool creates a dimension line that measures the radius of a circle or arc. It’s useful for indicating the size of circular or curved shapes.
- Diametric Dimension Tool: The Diametric Dimension tool creates a dimension line that measures the diameter of a circle or arc. It’s useful for indicating the overall size of circular or curved shapes.
- Angular Dimension Tool: The Angular Dimension tool creates a dimension line that measures the angle between two lines. It’s used to indicate the angle between lines, arcs, or other geometric elements.
- Ordinate Dimension Tool: The Ordinate Dimension tool creates dimension lines that measure the distance from a point to a reference line. It’s useful for indicating the position of objects relative to a specific reference point.
Annotation Tools
Annotation tools allow you to add text, symbols, and other information to your drawings. These tools are essential for providing clarity and detail to your designs, making them easier to understand and interpret.
- Text Tool: The Text tool allows you to add text to your drawings. You can create text boxes, insert text along a path, or create multiline text.
- Leader Tool: The Leader tool creates a line with an arrowhead that points to a specific object. You can use the Leader tool to add notes, dimensions, or other annotations to specific points on your drawing.
- Hatch Tool: The Hatch tool allows you to fill areas of your drawing with patterns. You can use the Hatch tool to create solid fills, patterned fills, or to represent different materials in your design.
- Block Tool: The Block tool allows you to create and insert custom symbols or groups of objects. Blocks are reusable elements that can be easily inserted into multiple drawings.
Creating Simple 2D and 3D Models
AutoCAD’s tools can be used to create both 2D and 3D models. Here are some examples:
2D Model: A Simple House Plan
- Use the Line tool to draw the Artikel of the house, including walls, doors, and windows.
- Use the Rectangle tool to create the floor plan, outlining the different rooms.
- Use the Circle tool to create circular features like windows or a fireplace.
- Use the Dimension tool to add measurements to the walls, doors, and windows.
- Use the Text tool to add labels for each room.
3D Model: A Simple Cube
- Use the Line tool to draw a square on the XY plane.
- Use the Extrude command to extrude the square into a cube. This command will extend the square vertically to create a three-dimensional shape.
- Use the 3D Orbit command to rotate the cube and view it from different angles.
AutoCAD Drawing Techniques
AutoCAD provides a wide range of tools and techniques for creating precise and complex drawings. Mastering these techniques is essential for creating professional-quality drawings and achieving desired results. This section will explore fundamental drawing techniques and concepts that form the foundation of effective AutoCAD usage.
Drawing Geometric Shapes, Autocad student
Drawing geometric shapes accurately is crucial for creating precise drawings. AutoCAD offers a variety of tools for creating lines, arcs, circles, and other geometric shapes.
- Lines: Lines are the most basic building blocks of any drawing. AutoCAD’s line tool allows you to draw straight lines by specifying start and end points. You can also use the line tool to draw multiple lines in a single command, extending the last line drawn.
- Arcs: Arcs are segments of circles. AutoCAD’s arc tool allows you to create arcs by specifying three points: start point, center point, and end point. You can also create arcs by specifying the start point, center point, and radius or by specifying the start point, end point, and radius.
- Circles: Circles are closed curves with a constant radius. AutoCAD’s circle tool allows you to create circles by specifying the center point and radius. You can also create circles by specifying two points on the circumference or by specifying a diameter.
- Polylines: Polylines are a series of connected line segments. AutoCAD’s polyline tool allows you to create polylines by specifying multiple points. You can also use the polyline tool to create curved segments, arcs, and other shapes.
- Rectangles: Rectangles are four-sided shapes with four right angles. AutoCAD’s rectangle tool allows you to create rectangles by specifying two corners or by specifying a center point and a width and height.
Layers
Layers are a fundamental concept in AutoCAD. They allow you to organize and manage drawing elements effectively by grouping objects with similar characteristics. Each layer has its own properties, such as color, line type, and line weight.
- Organizing Elements: Layers help organize drawing elements by grouping objects with similar characteristics. For example, you can create separate layers for walls, doors, windows, and furniture. This makes it easier to manage and modify your drawings.
- Visibility Control: Layers provide control over the visibility of objects. You can turn off or freeze specific layers to focus on specific elements of your drawing or to reduce clutter. This allows you to create clean and organized drawings.
- Properties Management: Layers allow you to apply specific properties, such as color, line type, and line weight, to objects. This helps ensure consistency and maintain a professional look in your drawings.
- Layer Management Tools: AutoCAD provides various tools for managing layers, including creating, deleting, renaming, and changing layer properties. These tools simplify the process of organizing and managing your drawing elements.
Combining Drawing Techniques
AutoCAD allows you to combine different drawing techniques to create complex drawings. For example, you can use the line tool to create the Artikel of a building, then use the arc tool to create rounded corners. You can then use the polyline tool to create the walls and the circle tool to create windows and doors.
- Complex Shapes: Combining drawing techniques allows you to create complex shapes that are not possible to create with a single tool. For example, you can use a combination of lines, arcs, and polylines to create a curved roof.
- Advanced Tools: AutoCAD offers advanced tools that can be used to create even more complex drawings. For example, the “Offset” tool allows you to create parallel lines or curves at a specified distance from an existing object. The “Trim” and “Extend” tools allow you to modify existing objects to create more complex shapes.
- Object Snaps: AutoCAD’s object snaps allow you to accurately snap to specific points on existing objects. This helps ensure that your drawings are precise and accurate. For example, you can snap to the midpoint of a line or the endpoint of an arc.
AutoCAD for 2D Design
AutoCAD is a powerful tool for creating 2D designs, and it finds applications in a wide range of industries. From architectural floor plans to mechanical drawings and electrical schematics, AutoCAD provides the tools and functionality needed to create precise and detailed designs.
Applications of AutoCAD in 2D Design
AutoCAD’s versatility makes it suitable for various 2D design applications. Here are some key areas where AutoCAD shines:
- Architectural Floor Plans: Architects use AutoCAD to create detailed floor plans for buildings, including layouts for rooms, furniture, and fixtures. AutoCAD’s tools allow for precise measurements, annotation, and the creation of complex shapes.
- Mechanical Drawings: Engineers rely on AutoCAD to create technical drawings of mechanical components, assemblies, and systems. These drawings include dimensions, tolerances, and material specifications, ensuring accuracy and clarity for manufacturing and assembly.
- Electrical Schematics: AutoCAD is used to create electrical diagrams, including circuit schematics, wiring diagrams, and panel layouts. These diagrams use symbols and lines to represent electrical components and their connections, facilitating understanding and troubleshooting.
- Civil Engineering Drawings: AutoCAD is widely used in civil engineering for creating site plans, road layouts, and utility plans. It helps engineers visualize and plan infrastructure projects, ensuring accurate representation of terrain, structures, and utilities.
Creating 2D Drawings in AutoCAD
Creating 2D drawings in AutoCAD involves a systematic process that leverages its comprehensive tools:
- Sketching and Drawing: The process begins with sketching the basic shape of the object using drawing tools like lines, arcs, circles, and polygons. AutoCAD allows for precise control over dimensions and geometry.
- Dimensioning: Once the basic shape is established, dimensions are added to define the size and location of elements within the drawing. AutoCAD offers various dimensioning tools for linear, angular, and radial dimensions.
- Annotation: Text and symbols are used to annotate the drawing, providing additional information such as material specifications, tolerances, and notes. AutoCAD provides tools for adding text, leaders, and blocks for annotations.
- Hatching: Hatching patterns are used to fill areas of the drawing, representing different materials or textures. AutoCAD offers a wide range of hatching patterns, allowing for customization and visual clarity.
- Layers: Layers are used to organize and manage different elements within the drawing. By grouping related elements on specific layers, designers can easily control visibility and make changes without affecting other parts of the drawing.
Real-World Examples of 2D Design Projects
AutoCAD’s capabilities are demonstrated in countless real-world projects across various industries. Here are some examples:
- Architectural Design: The Burj Khalifa, the world’s tallest building, was designed using AutoCAD. The software played a crucial role in creating the intricate floor plans, structural details, and façade designs for this iconic structure.
- Mechanical Engineering: Boeing uses AutoCAD for designing and manufacturing its aircraft. From the intricate components of jet engines to the complex structures of aircraft fuselages, AutoCAD provides the tools for precision and accuracy.
- Electrical Engineering: The electrical system of the International Space Station was designed using AutoCAD. The software enabled engineers to create detailed schematics and diagrams, ensuring the safe and reliable operation of the station’s power systems.
AutoCAD for 3D Modeling
AutoCAD offers a robust set of tools for creating and manipulating 3D models. This module will introduce the fundamentals of 3D modeling in AutoCAD, exploring the different methods and techniques for generating complex 3D shapes.
Understanding 3D Modeling Concepts
AutoCAD provides several approaches to 3D modeling, each suited for different applications and design needs. These approaches are categorized as solids, surfaces, and mesh modeling.
- Solid Modeling: Solid modeling creates 3D objects with a defined volume and material properties. This method ensures that the model is completely enclosed, with no gaps or holes. Solid modeling is often used for creating objects with complex geometry, such as mechanical parts, architectural structures, and industrial products.
- Surface Modeling: Surface modeling focuses on creating 3D objects by defining their surfaces. This method allows for the creation of smooth, curved shapes and can be used for designing products with intricate details, such as car bodies, furniture, and jewelry.
- Mesh Modeling: Mesh modeling involves creating 3D objects by defining a network of points, lines, and polygons. This method is often used for creating organic shapes, such as characters, landscapes, and terrain. Mesh modeling provides flexibility in creating complex and detailed models, but it may require more computational power.
Creating 3D Models in AutoCAD
AutoCAD offers a variety of tools for creating 3D models, including extrude, revolve, and sweep. These tools allow users to generate shapes by manipulating existing 2D geometries or creating new 3D objects directly.
- Extrude: The extrude command takes a 2D shape and extends it in a specified direction, creating a 3D object with a uniform cross-section. This method is commonly used for creating simple shapes like boxes, cylinders, and prisms.
- Revolve: The revolve command takes a 2D profile and rotates it around a specified axis, creating a 3D object with a rotational symmetry. This method is useful for creating objects like cones, spheres, and toruses.
- Sweep: The sweep command takes a 2D profile and moves it along a specified path, creating a 3D object with a variable cross-section. This method allows for creating complex shapes with varying geometries, such as curved surfaces, pipes, and ribbons.
Examples of 3D Models Created Using AutoCAD
AutoCAD’s versatility in 3D modeling enables the creation of various complex objects, showcasing its capabilities across different industries.
- Mechanical Design: AutoCAD is used to design and model complex mechanical parts, including gears, bearings, and engines. The software’s precision and accuracy ensure the creation of functional and reliable components for various industries.
- Architectural Design: Architects use AutoCAD to create detailed 3D models of buildings, interiors, and landscapes. This allows for visualization of the design, analysis of space, and efficient collaboration with clients and contractors.
- Industrial Design: Industrial designers utilize AutoCAD to create 3D models of consumer products, ranging from furniture and appliances to automobiles and electronics. The software’s modeling capabilities enable the creation of aesthetically pleasing and functional designs.
AutoCAD for Visualization and Rendering: Autocad Student

In the world of design, conveying your ideas effectively is crucial. AutoCAD, beyond its 2D and 3D modeling capabilities, offers powerful tools for visualization and rendering, allowing you to create realistic representations of your designs. These visualizations play a vital role in communicating your design intent, showcasing the final product, and gaining client approval.
Rendering Techniques
Rendering techniques in AutoCAD are diverse, each contributing to the creation of visually compelling presentations.
- Photorealistic Rendering: This technique uses advanced algorithms to simulate light and shadow interactions, creating images that closely resemble photographs. It allows you to showcase the material properties, textures, and lighting effects of your design, providing a highly realistic representation.
- Wireframe Visualization: This technique presents a skeletal representation of the design, outlining its lines and edges. It’s often used for early design stages, allowing for quick visualization of the basic form and structure without the complexity of photorealistic rendering.
Examples of Rendered Images and Animations
AutoCAD’s rendering capabilities allow for the creation of stunning images and animations, transforming designs into captivating visual experiences.
- Architectural Renderings: Imagine a high-rise building rendered with photorealistic accuracy, showcasing the intricate details of its facade, the play of light and shadow on its windows, and the surrounding cityscape. AutoCAD’s rendering tools allow architects to create such immersive visuals, providing a compelling glimpse into the finished product.
- Product Design Renderings: Imagine a sleek new car model rendered in AutoCAD, showcasing its curves, lines, and materials in photorealistic detail. The rendering captures the car’s design language, highlighting its aesthetics and functionality.
- Animations: AutoCAD can be used to create dynamic animations, showcasing the movement and interaction of design elements. For example, an animation could illustrate the operation of a mechanical device, providing a clear understanding of its functionality.
AutoCAD for Collaboration and Sharing
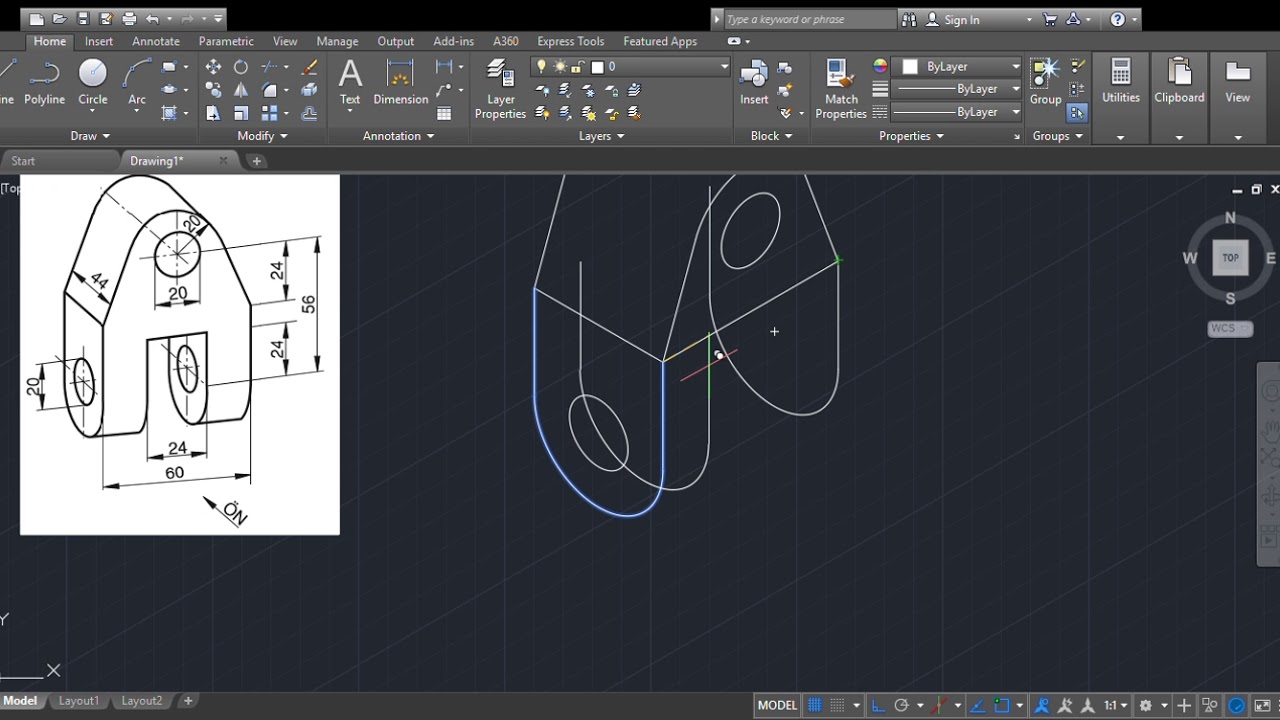
AutoCAD projects often involve collaboration with other users, making it essential to understand how to share and manage drawing files effectively. This section explores various methods for sharing AutoCAD drawings and demonstrates how to utilize tools for collaborative work.
Sharing AutoCAD Drawings
Sharing AutoCAD drawings is crucial for teamwork and project management. Different methods cater to various collaboration needs, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
- Cloud Storage: Cloud storage platforms like Dropbox, Google Drive, and OneDrive offer convenient and secure ways to store and share AutoCAD drawings. Users can access and edit files from any location with an internet connection, facilitating real-time collaboration.
- Email Attachments: Emailing AutoCAD drawings as attachments is a straightforward method for sharing files. However, it’s important to note that file sizes can be large, potentially leading to email delivery issues. Consider compressing the files or using file-sharing services for larger drawings.
- External File Formats: AutoCAD allows exporting drawings to various external formats, such as DWG, DXF, PDF, and image files. This flexibility enables sharing with users who may not have AutoCAD installed, promoting wider accessibility.
Collaborating on AutoCAD Projects
AutoCAD offers powerful tools for collaborating on projects, enabling multiple users to work simultaneously on a single drawing.
- External References (Xrefs): Xrefs allow you to link separate drawings into a main drawing, creating a hierarchical structure. Changes made to the referenced drawing automatically update in the main drawing, fostering efficient collaboration.
- Layers: Layers organize drawing elements, facilitating collaboration by allowing different users to work on specific aspects of a project without interfering with each other’s work. For instance, one user might work on the architectural plan on a dedicated layer, while another user focuses on the electrical layout on a separate layer.
AutoCAD for Student Projects
AutoCAD is a powerful tool that can be used to create a wide range of projects, from simple drawings to complex 3D models. As a student, you can use AutoCAD to bring your ideas to life and showcase your skills in various disciplines. This section will explore ways to utilize AutoCAD for student projects, providing guidance on project planning, execution, and presentation techniques.
Project Ideas for Different Disciplines
Student projects using AutoCAD can span across diverse disciplines, showcasing the versatility of the software. Here are some ideas categorized by field:
- Architecture:
- Design a sustainable home incorporating passive solar design and energy-efficient features.
- Create a conceptual design for a community center, focusing on accessibility and inclusivity.
- Develop a detailed floor plan and elevation drawings for a multi-story apartment building.
- Engineering:
- Model a mechanical component, such as a gear system or a pump, and analyze its performance using AutoCAD’s simulation features.
- Design a bridge structure, considering load distribution and material properties.
- Create a detailed schematic diagram for an electrical circuit or a control system.
- Design:
- Design a product, such as a furniture piece or a consumer product, considering ergonomics and aesthetics.
- Create a 3D model of a logo or a brand identity for a fictional company.
- Develop a layout for a website or a mobile application, incorporating user interface design principles.
Project Planning and Execution
Effective project planning and execution are crucial for success in any AutoCAD project. Consider the following steps:
- Define Project Scope: Clearly Artikel the project objectives, deliverables, and timeline.
- Gather Resources: Identify the necessary software, hardware, and reference materials for the project.
- Develop a Work Plan: Break down the project into manageable tasks and assign deadlines for each.
- Utilize AutoCAD Features: Explore AutoCAD’s tools and features to optimize your workflow and enhance project efficiency.
- Document and Review: Regularly save your work, create backups, and review your progress to ensure accuracy and meet project goals.
Presentation Techniques
Presenting your AutoCAD project effectively is essential for showcasing your work and conveying your ideas. Consider these techniques:
- Visual Appeal: Use clear and concise drawings, with appropriate annotations and labels.
- 3D Modeling: Incorporate 3D models to enhance visual understanding and demonstrate the project’s functionality.
- Rendering: Use rendering techniques to create realistic visuals that highlight the project’s design and aesthetics.
- Technical Details: Include technical specifications, dimensions, and material details to provide comprehensive information.
- Clear Communication: Present your project with a clear and concise narrative, explaining the design decisions and the project’s impact.
Examples of Successful Student Projects
- Sustainable Housing Design: A student project focused on designing a net-zero energy home, incorporating solar panels, green roofs, and efficient building materials. The project showcased the student’s understanding of sustainable design principles and AutoCAD’s capabilities in creating detailed architectural drawings.
- Robotic Arm Design: An engineering student designed a robotic arm using AutoCAD, focusing on kinematics and motion control. The project demonstrated the student’s ability to model complex mechanical systems and analyze their performance.
- Interactive Website Design: A design student created a prototype for an interactive website using AutoCAD, incorporating user interface elements and visual design principles. The project showcased the student’s understanding of website design and AutoCAD’s capabilities in creating visual prototypes.
AutoCAD Resources and Support
Learning AutoCAD can be a rewarding experience, but it can also present challenges along the way. Thankfully, there are numerous resources and support systems available to help students navigate the learning curve and succeed in their AutoCAD journey.
Online Resources
The internet offers a vast array of resources for AutoCAD learners, providing access to tutorials, documentation, and community forums. These online resources are invaluable for students seeking to deepen their understanding of AutoCAD concepts, explore advanced techniques, and troubleshoot issues they encounter.
- Autodesk Knowledge Network: Autodesk, the developer of AutoCAD, offers a comprehensive knowledge base, known as the Autodesk Knowledge Network. This platform provides access to extensive documentation, tutorials, and troubleshooting guides, covering various aspects of AutoCAD, from basic commands to advanced modeling techniques.
- Online Tutorials: Numerous online platforms offer free and paid tutorials specifically designed for AutoCAD learners. These tutorials often provide step-by-step instructions, practical exercises, and real-world examples, making it easier for students to grasp key concepts and apply them in their projects.
- Community Forums: Online communities dedicated to AutoCAD are vibrant hubs for learners to connect with fellow students, experienced users, and industry professionals. These forums allow students to ask questions, share their experiences, and learn from others’ insights. Popular platforms include Autodesk Community, Reddit’s r/AutoCAD, and various AutoCAD-specific forums.
Seeking Support
When facing challenges in AutoCAD, seeking support from instructors, mentors, or online communities can be crucial. Reaching out for assistance allows students to gain clarity on specific issues, explore alternative solutions, and receive guidance from experienced users.
- Instructors and Mentors: Students enrolled in formal AutoCAD courses can leverage the expertise of their instructors or mentors. These individuals are often well-versed in AutoCAD and can provide personalized guidance, address specific challenges, and offer valuable feedback on student projects.
- Online Communities: Online communities offer a platform for students to connect with a broader network of AutoCAD users. By posting questions or participating in discussions, students can tap into the collective knowledge and experience of the community, often receiving insightful answers and solutions from experienced users.
AutoCAD Applications in Different Fields
AutoCAD is a powerful and versatile software that finds applications in a wide range of industries. Its ability to create detailed drawings, models, and visualizations makes it an indispensable tool for architects, engineers, designers, and manufacturers. The diverse functionalities of AutoCAD cater to the specific requirements of different fields, enabling efficient workflows and enhanced productivity.
Architecture
AutoCAD is extensively used in the field of architecture for creating detailed building plans, elevations, sections, and 3D models. Architects use AutoCAD to design and visualize buildings, incorporating features like walls, doors, windows, and furniture. They can also create site plans, landscaping designs, and interior layouts.
- Features: AutoCAD’s drawing tools, layers, and annotation features enable architects to create precise and detailed architectural drawings. The 3D modeling capabilities allow them to visualize buildings from different perspectives and create realistic renderings.
- Examples: AutoCAD is used in the design of iconic structures like the Burj Khalifa in Dubai and the Guggenheim Museum in Bilbao, Spain.
Engineering
AutoCAD plays a crucial role in various engineering disciplines, including mechanical, civil, and electrical engineering. Engineers use AutoCAD to design and document mechanical components, structures, and electrical systems.
- Features: AutoCAD’s drafting tools, parametric modeling capabilities, and analysis features are essential for engineers. They can create detailed drawings of mechanical parts, structural plans, and electrical schematics.
- Examples: AutoCAD is used in the design of bridges, airplanes, and complex machinery.
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing industry, AutoCAD is used for creating detailed drawings of products, machinery, and tooling. It facilitates the production process by providing accurate and consistent designs.
- Features: AutoCAD’s precision drawing tools, dimensioning capabilities, and ability to generate manufacturing data are crucial for manufacturing applications. It enables manufacturers to create production drawings, assembly instructions, and tool path data.
- Examples: AutoCAD is used in the design and manufacture of automobiles, electronics, and consumer products.
Design
AutoCAD is a popular tool for graphic designers, interior designers, and industrial designers. It allows them to create professional-quality drawings, illustrations, and visualizations.
- Features: AutoCAD’s drawing tools, text editing capabilities, and image manipulation features are used for creating logos, brochures, and product designs. Its 3D modeling capabilities enable designers to visualize and create complex designs.
- Examples: AutoCAD is used in the design of product packaging, website layouts, and marketing materials.
Future Trends in AutoCAD
AutoCAD, a leading computer-aided design (CAD) software, is constantly evolving to adapt to the ever-changing landscape of design and engineering. Emerging technologies are transforming the way we design, collaborate, and visualize, and AutoCAD is embracing these trends to remain at the forefront of the industry.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is revolutionizing various industries, and CAD is no exception. AutoCAD is incorporating AI capabilities to enhance its functionality and streamline design processes.
- Automated Design Suggestions: AI algorithms can analyze design parameters and provide intelligent suggestions, helping users optimize their designs for efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- Design Optimization: AI can analyze large datasets of design information to identify patterns and suggest improvements, leading to more robust and efficient designs.
- Error Detection and Prevention: AI-powered tools can detect potential errors and inconsistencies in designs, preventing costly mistakes and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
These AI-driven features are transforming AutoCAD into a more intelligent and user-friendly tool, empowering designers to work smarter and faster.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
VR and AR technologies are bridging the gap between the digital and physical worlds, enabling designers to experience their creations in immersive environments.
- Realistic Design Visualization: VR and AR allow designers to visualize their designs in a realistic 3D environment, providing a more comprehensive understanding of the project’s scale, proportions, and spatial relationships.
- Collaborative Design Reviews: VR and AR facilitate collaborative design reviews, allowing stakeholders to interact with the design in real-time and provide feedback in a more engaging and intuitive way.
- On-Site Design Visualization: AR can overlay digital designs onto the real world, enabling designers to visualize how their designs will fit into the existing environment, aiding in site planning and construction.
VR and AR are transforming the way we design, collaborate, and visualize, making AutoCAD a more powerful tool for creating innovative and immersive experiences.
Cloud-Based Platforms
Cloud computing is enabling designers to access and share design data anytime, anywhere.
- Remote Collaboration: Cloud-based platforms allow designers to work collaboratively on projects from different locations, facilitating seamless communication and data sharing.
- Data Security and Backup: Cloud storage ensures data security and provides automatic backups, reducing the risk of data loss and ensuring data integrity.
- Scalability and Accessibility: Cloud-based platforms offer scalability, allowing designers to access the resources they need without the limitations of traditional hardware infrastructure.
Cloud technology is transforming the way we design and collaborate, making AutoCAD more accessible, efficient, and secure.
Closing Summary
As you delve deeper into AutoCAD, you’ll discover a world of possibilities for creating innovative designs, visualizing complex structures, and collaborating effectively with others. Whether you’re working on personal projects or pursuing a career in design, the skills you acquire through AutoCAD will be invaluable assets.
As an AutoCAD student, you’re likely focused on mastering the technical aspects of design. However, understanding the principles of software testing can be beneficial too. Gaining a solid foundation in software testing through the ISTQB Foundation Level certification can enhance your ability to create robust and reliable AutoCAD designs.
