Autodesk AutoCAD stands as a cornerstone in the world of design and engineering, empowering professionals across industries to bring their ideas to life. Its history spans decades, witnessing its evolution into a comprehensive suite of tools that cater to diverse needs, from architectural blueprints to intricate mechanical components.
Table of Contents
AutoCAD’s versatility shines through its ability to handle both 2D drafting and 3D modeling, offering a platform for creating detailed drawings, crafting realistic visualizations, and even simulating real-world scenarios. This software’s intuitive interface and extensive library of tools make it accessible to both seasoned professionals and aspiring designers, fostering creativity and innovation.
Introduction to Autodesk AutoCAD
Autodesk AutoCAD is a powerful computer-aided design (CAD) software widely used for 2D and 3D design and drafting. It has been a cornerstone of the design and engineering industries for over four decades, revolutionizing the way professionals create and visualize their ideas.
AutoCAD’s versatility and comprehensive features make it suitable for a wide range of industries, including architecture, engineering, construction, manufacturing, and more. Its applications span from designing buildings and bridges to creating intricate mechanical parts and developing complex electrical schematics.
Key Features and Functionalities
AutoCAD offers a wide array of features that empower users to create and manipulate designs with precision and efficiency. Some of the key functionalities include:
- Drawing and Drafting: AutoCAD provides a comprehensive set of tools for creating and editing 2D and 3D drawings. Users can draw lines, arcs, circles, and other geometric shapes with precise control over dimensions and properties.
- Modeling: AutoCAD enables users to create 3D models of objects and assemblies. Users can utilize various modeling tools, such as extrusion, revolution, and sweeping, to build complex geometries.
- Annotation and Dimensioning: AutoCAD provides tools for adding annotations, dimensions, and other text-based information to drawings. This ensures clarity and accuracy in design documentation.
- Collaboration and Sharing: AutoCAD facilitates collaboration among designers and engineers. Users can share their drawings and models with others, enabling seamless teamwork and project management.
- Customization and Automation: AutoCAD offers extensive customization options, allowing users to tailor the software to their specific needs. This includes creating custom tools, macros, and scripts to automate repetitive tasks.
AutoCAD Versions and Editions
AutoCAD is a powerful software suite with various versions and editions catering to diverse user needs. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for choosing the right version for your specific requirements.
AutoCAD Versions
The different versions of AutoCAD represent major updates released over time. Each version incorporates new features, enhancements, and improvements over its predecessors.
- AutoCAD 2024: The latest version, offering enhanced collaboration features, improved 3D modeling tools, and advanced visualization capabilities. It incorporates new features like generative design, improved cloud connectivity, and a streamlined user interface.
- AutoCAD 2023: Introduced features like the new “AutoCAD for Web” service for cloud-based design and collaboration. This version also brought enhancements to 3D modeling, visualization, and drawing management.
- AutoCAD 2022: This version introduced new features like the “AutoCAD for Web” service, allowing users to access and work on drawings from any device with an internet connection. It also introduced improvements to 3D modeling, visualization, and drawing management.
- AutoCAD 2021: Focused on enhancing collaboration and workflow efficiency. This version introduced features like the “AutoCAD for Web” service, allowing users to access and work on drawings from any device with an internet connection. It also introduced improvements to 3D modeling, visualization, and drawing management.
AutoCAD Editions
AutoCAD offers various editions tailored to different user profiles and industry requirements. Each edition includes a specific set of features and functionalities.
- AutoCAD LT: A cost-effective option designed for individuals and small businesses requiring basic 2D drafting and design capabilities. It includes essential drawing tools, but lacks advanced features like 3D modeling, rendering, and customization options.
- AutoCAD: The standard edition, offering a comprehensive set of 2D and 3D design tools, suitable for architects, engineers, and designers working on a wide range of projects. It includes features like 3D modeling, rendering, and customization options.
- AutoCAD Architecture: Specialized for architects, this edition includes tools for building information modeling (BIM), architectural design, and documentation. It offers features like wall and roof design, space planning, and energy analysis.
- AutoCAD MEP: Designed for mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) engineers, this edition provides tools for designing and documenting MEP systems. It includes features like electrical circuit design, pipe routing, and HVAC system analysis.
- AutoCAD Civil 3D: Targeted at civil engineers, this edition offers tools for designing and analyzing civil infrastructure projects. It includes features like site planning, road design, and drainage analysis.
- AutoCAD Plant 3D: Specialized for plant design, this edition includes tools for designing and documenting process plants. It offers features like piping design, equipment placement, and plant layout.
- AutoCAD Map 3D: Designed for GIS professionals, this edition provides tools for creating, managing, and analyzing geographic data. It includes features like map creation, data analysis, and spatial referencing.
Comparing AutoCAD Versions and Editions
| Feature | AutoCAD LT | AutoCAD | AutoCAD Architecture | AutoCAD MEP | AutoCAD Civil 3D | AutoCAD Plant 3D | AutoCAD Map 3D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2D Drafting | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 3D Modeling | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Rendering | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Customization | Limited | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Industry-Specific Tools | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
AutoCAD Interface and User Experience
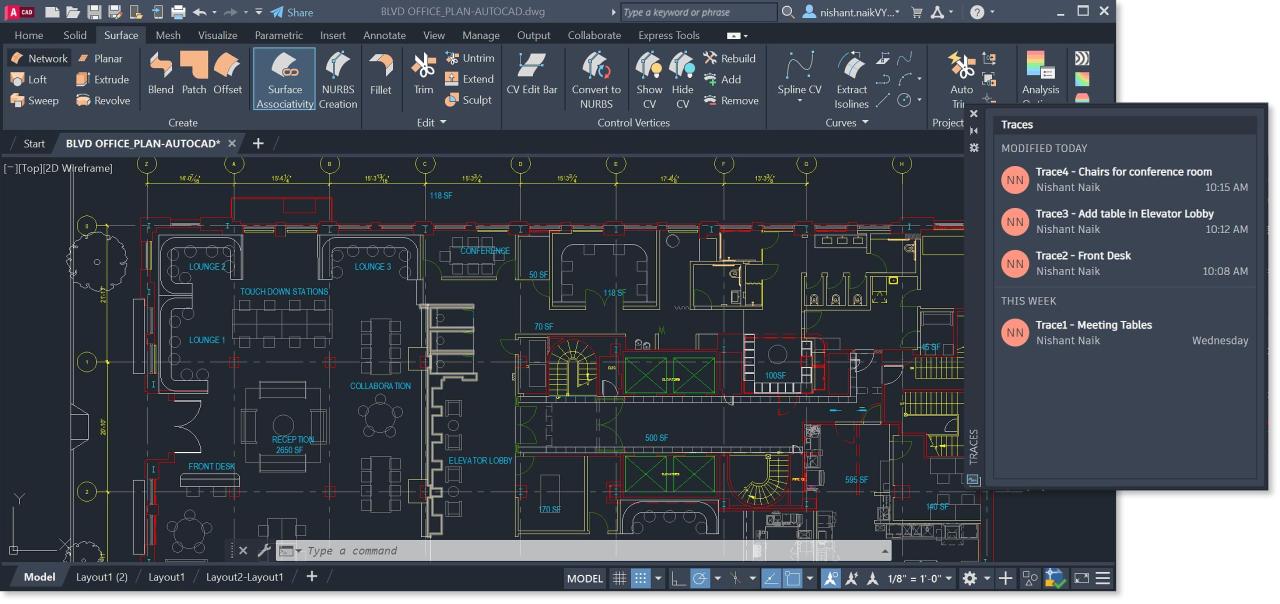
AutoCAD’s user interface (UI) is designed to be intuitive and efficient for users of all skill levels. It provides a comprehensive set of tools and features for creating, editing, and managing 2D and 3D drawings.
The AutoCAD Interface Layout
The AutoCAD interface is divided into several key components, each serving a specific purpose.
- Ribbon: The ribbon is located at the top of the interface and contains tabs for different functionalities. Each tab groups related tools and commands, making it easy to find what you need.
- Toolbars: Toolbars provide quick access to frequently used commands and tools. They can be customized to include the tools you use most often.
- Command Line: The command line is located at the bottom of the interface and allows you to enter commands directly. It provides a more flexible and powerful way to interact with AutoCAD.
- Drawing Area: The drawing area is the central part of the interface where you create and edit your drawings. It displays the current drawing, including objects, layers, and other elements.
- Status Bar: The status bar is located at the bottom of the interface and provides information about the current drawing, such as coordinates, snap settings, and object properties.
Workflow and Navigation in AutoCAD
AutoCAD’s workflow involves a series of steps to create and manage drawings effectively.
- Start a New Drawing: Begin by creating a new drawing file. You can choose from various drawing templates to set up your drawing environment.
- Draw Objects: Use the drawing tools to create objects such as lines, circles, arcs, and polygons. You can also import objects from other files or use pre-defined blocks.
- Modify Objects: Modify objects using tools like move, copy, rotate, scale, and trim. You can also use the command line to perform more complex modifications.
- Dimensioning and Annotations: Add dimensions, text, and other annotations to your drawing to provide information about the design. You can use various dimension styles and text formats.
- Layers and Colors: Organize your drawing by using layers and colors to group objects and control their visibility.
- Saving and Printing: Save your drawing in AutoCAD’s native DWG format. You can also export your drawing in various formats, such as PDF, DXF, and JPG. You can print your drawing to a physical plotter or printer.
User Experience in AutoCAD
AutoCAD provides a powerful and versatile environment for creating and managing drawings. However, its user experience can be challenging for beginners due to its complexity.
- Strengths:
- Powerful Toolset: AutoCAD offers a comprehensive set of tools for creating and editing drawings.
- Customization: The interface can be customized to suit individual preferences.
- Industry Standard: AutoCAD is widely used in various industries, making it a valuable skill to have.
- Extensive Support: AutoCAD has a large user community and abundant online resources for learning and support.
- Weaknesses:
- Steep Learning Curve: Mastering AutoCAD requires significant time and effort.
- Complex Interface: The interface can be overwhelming for new users.
- High Cost: AutoCAD is a paid software, which can be a barrier for some users.
2D Drafting and Design: Autodesk Autocad
AutoCAD is a powerful tool for creating precise 2D drawings and designs. Its comprehensive set of tools allows users to easily create, edit, and manipulate geometric shapes, lines, and curves, making it suitable for various industries and applications.
Creating and Editing Geometric Shapes
Creating and editing geometric shapes in AutoCAD involves using a variety of tools and commands. The process begins with defining the desired shape’s parameters, such as its size, position, and orientation. Once defined, the shape can be drawn, modified, and manipulated to meet the specific requirements of the design.
- Lines and Points: The Line command allows users to draw straight lines by specifying two points. The Point command creates individual points that can be used as reference points for other drawing elements.
- Circles and Arcs: AutoCAD provides tools for drawing circles and arcs. The Circle command creates a circle by specifying its center point and radius, while the Arc command allows users to create arcs by defining their start and end points and radius.
- Rectangles and Polygons: The Rectangle command creates rectangular shapes by specifying two diagonal corners, while the Polygon command allows users to create polygons with any number of sides.
- Splines and Curves: AutoCAD offers tools for creating smooth, curved lines. The Spline command creates curves that pass through specified points, while the Curve command allows users to create curves by defining their control points.
Editing Geometric Shapes
Once a shape is created, users can modify it using various editing tools. These tools allow for precise adjustments to shape size, position, and orientation.
- Move and Copy: The Move command allows users to relocate objects to a new location, while the Copy command creates duplicate objects at a specified distance.
- Scale and Rotate: The Scale command changes the size of an object, while the Rotate command rotates an object around a specified point.
- Trim and Extend: The Trim command removes portions of objects that extend beyond a specified boundary, while the Extend command extends objects to meet a specified boundary.
- Offset and Mirror: The Offset command creates parallel copies of objects at a specified distance, while the Mirror command creates symmetrical copies of objects across a specified line.
2D Drafting and Design Applications
2D drafting and design applications using AutoCAD are prevalent across various industries.
- Architecture: AutoCAD is used to create floor plans, elevations, and sections of buildings. Architects utilize its precise drawing tools and annotation features to create detailed blueprints for construction.
- Engineering: Engineers use AutoCAD to design mechanical parts, electrical circuits, and civil infrastructure projects. Its ability to handle complex geometries and create technical drawings makes it an essential tool for engineering design.
- Manufacturing: AutoCAD is used to design and create manufacturing drawings, including parts, assemblies, and tooling. Its precision and accuracy are crucial for ensuring the successful production of manufactured goods.
- Construction: AutoCAD is used to create construction drawings, including site plans, elevations, and sections. Its ability to manage large-scale projects and integrate with other software applications makes it an invaluable tool for construction professionals.
3D Modeling and Visualization
AutoCAD is not just a 2D drafting tool; it also offers powerful capabilities for creating and visualizing 3D models. This allows you to design and analyze complex objects from all angles, bringing your ideas to life in a realistic and interactive way.
3D Modeling Techniques
AutoCAD provides a range of tools and techniques for building 3D models, allowing you to create objects of various shapes and complexities. Some of the most commonly used techniques include:
* Extrusion: This involves creating a 3D object by extending a 2D shape along a specified direction. For example, you can extrude a rectangle to create a cube or a circle to create a cylinder.
* Revolving: This technique involves rotating a 2D profile around an axis to create a 3D object. For example, you can revolve a line segment to create a cone or a rectangle to create a torus.
* Sweeping: This method involves moving a 2D profile along a path to create a 3D object. For example, you can sweep a circle along a line to create a curved surface or a rectangle along a curve to create a complex shape.
Rendering and Visualization
Once you have created your 3D model, you can use AutoCAD’s rendering tools to create realistic visualizations. This allows you to see how your design will look in a real-world environment, complete with lighting, shadows, and textures. AutoCAD offers a variety of rendering options, including:
* Ray tracing: This technique simulates the way light interacts with objects in the real world, producing highly realistic images.
* Photorealistic rendering: This option creates images that look like photographs, capturing the details of your model and its environment.
* Shaded rendering: This method creates a simple, shaded representation of your model, highlighting its form and shape.
Rendering is a powerful tool for communicating your design ideas to clients, colleagues, and stakeholders. It allows you to present your work in a compelling and engaging way, fostering understanding and collaboration.
Using 3D Models in AutoCAD
3D models in AutoCAD are not just for visualization; they can also be used for various other purposes:
* Analysis: You can analyze the properties of your 3D model, such as its volume, surface area, and center of gravity.
* Simulation: You can simulate real-world scenarios, such as the flow of air around a building or the movement of a machine part.
* Collaboration: You can share your 3D models with others, enabling them to view, edit, and collaborate on your designs.
AutoCAD Customization and Automation
AutoCAD offers a range of customization options and programming features that allow users to tailor the software to their specific needs and automate repetitive tasks. These capabilities can significantly enhance productivity and streamline workflows.
AutoCAD Customization Options
AutoCAD provides several ways to customize its behavior and appearance.
- Custom Settings: AutoCAD offers a wide range of customizable settings, including drawing units, grid settings, and display options. These settings can be accessed through the Options dialog box and saved as custom profiles for different projects or users.
- Customizable Toolbars and Menus: Users can create custom toolbars and menus to access frequently used commands and tools. This allows for a more personalized and efficient user interface.
- Macros: Macros are sequences of commands that can be recorded and played back to automate repetitive tasks. They are simple to create and use, making them ideal for automating tasks such as creating layers, setting dimensions, or applying specific styles.
- Scripts: Scripts are more advanced automation tools that use the AutoLISP programming language. They provide more flexibility and control than macros, allowing users to create complex automated processes.
Automating Repetitive Tasks
AutoCAD’s programming features enable users to automate repetitive tasks and streamline workflows.
- AutoLISP: AutoLISP is a powerful programming language that allows users to create custom functions, manipulate objects, and interact with the AutoCAD environment. It can be used to automate tasks such as creating blocks, hatching areas, or extracting data from drawings.
- Visual LISP: Visual LISP is a graphical interface for AutoLISP that simplifies the development process. It provides a visual editor, debugging tools, and other features that make it easier to write and test AutoLISP code.
- AutoCAD VBA: VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) is a programming language that can be used to automate tasks within AutoCAD. It allows users to access and manipulate AutoCAD objects and commands through a familiar programming environment.
- .NET API: AutoCAD’s .NET API provides a more object-oriented approach to programming, allowing developers to create powerful and complex automation solutions.
Examples of Customized Workflows and Automated Processes, Autodesk autocad
- Automated Drafting: Scripts can be used to automate the creation of standard drawing elements, such as walls, doors, and windows. This can significantly reduce the time required to create detailed drawings.
- Batch Processing: VBA or .NET API can be used to automate the processing of multiple drawings, such as applying specific styles, extracting data, or generating reports.
- Custom Tool Creation: AutoLISP or VBA can be used to create custom tools that perform specific tasks, such as calculating areas, creating complex geometries, or generating 3D models.
- Data Extraction and Analysis: Scripts can be used to extract data from drawings and perform analysis, such as calculating quantities, generating reports, or creating visualizations.
Industry-Specific Applications of AutoCAD
AutoCAD’s versatility extends beyond basic drafting and design, making it an indispensable tool across various industries. Its powerful features and customization options cater to specific workflows and requirements, enabling professionals to streamline processes and achieve optimal results.
Architecture
AutoCAD plays a pivotal role in architectural design and planning. Architects use AutoCAD to create detailed floor plans, elevations, sections, and 3D models of buildings.
- Building Information Modeling (BIM): AutoCAD integrates seamlessly with BIM software, allowing architects to create intelligent models that contain detailed information about building components. This facilitates collaboration among different stakeholders and enables accurate cost estimations and material management.
- Site Planning and Layout: Architects use AutoCAD to design site plans, including landscaping, parking areas, and utilities. They can create accurate representations of the site, ensuring efficient space utilization and compliance with regulations.
- Rendering and Visualization: AutoCAD’s rendering capabilities allow architects to create realistic visualizations of their designs. This helps clients visualize the final project and provides valuable feedback during the design process.
Engineering
AutoCAD is widely used in various engineering disciplines, including mechanical, civil, and electrical engineering.
- Mechanical Engineering: Mechanical engineers use AutoCAD to design and document mechanical components, assemblies, and systems. They leverage AutoCAD’s advanced drafting tools to create precise drawings and technical specifications. AutoCAD’s parametric modeling capabilities enable engineers to easily modify designs and explore different options.
- Civil Engineering: Civil engineers rely on AutoCAD for infrastructure projects, such as roads, bridges, and tunnels. AutoCAD’s tools for surveying, site planning, and drafting enable them to create accurate representations of the terrain and design infrastructure projects that meet safety and efficiency standards.
- Electrical Engineering: Electrical engineers use AutoCAD to design electrical systems, including wiring diagrams, circuit layouts, and panel schematics. AutoCAD’s symbol libraries and automation features streamline the design process and ensure accuracy in electrical drawings.
Manufacturing
AutoCAD is an essential tool for manufacturing companies, enabling them to design, manufacture, and document products.
- Product Design: Manufacturers use AutoCAD to create detailed 3D models of their products, allowing them to visualize and analyze designs before production. AutoCAD’s parametric modeling capabilities enable engineers to make design changes easily and explore different design options.
- Manufacturing Drawings: AutoCAD is used to create precise manufacturing drawings that provide all the necessary information for production. These drawings include dimensions, tolerances, materials, and other critical details. AutoCAD’s automation features streamline the creation of drawings and ensure consistency across the manufacturing process.
- CAM Integration: AutoCAD integrates seamlessly with computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software, enabling manufacturers to generate toolpaths for CNC machines directly from their AutoCAD designs. This streamlined workflow reduces errors and improves efficiency in the manufacturing process.
Integration with Other Autodesk Products
AutoCAD’s strength lies not only in its individual capabilities but also in its seamless integration with other Autodesk products. This interconnectedness allows for a streamlined workflow, enhanced data sharing, and improved project efficiency.
Interoperability and Data Sharing
AutoCAD’s ability to work seamlessly with other Autodesk products fosters a collaborative environment where data flows freely between different software solutions. This interoperability is crucial for projects involving multiple disciplines, enabling architects, engineers, and construction professionals to work on the same project with consistent data.
- Revit: AutoCAD can import and export data in various formats, including DWG, allowing for smooth transitions between 2D drafting and 3D modeling. This integration enables architects to create detailed 2D drawings in AutoCAD and then import them into Revit for building information modeling (BIM) purposes. This workflow facilitates efficient coordination between architects and engineers, ensuring consistency and accuracy across all project phases.
- Civil 3D: AutoCAD’s integration with Civil 3D, a software specifically designed for civil engineering projects, enables users to transfer design data between the two platforms. This interoperability allows for a seamless workflow, where civil engineers can create and modify designs in Civil 3D and then export them to AutoCAD for further detailing or visualization. This process streamlines the design and documentation process, ensuring that all project stakeholders have access to the latest information.
Benefits of Integrated Workflows
Utilizing AutoCAD in conjunction with other Autodesk software solutions offers numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Collaboration: The seamless data sharing between AutoCAD and other Autodesk products fosters a collaborative environment, allowing different disciplines to work on the same project with consistent data. This reduces errors and misunderstandings, ensuring that everyone is working with the same information.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Integrated workflows streamline project processes, reducing the need for manual data transfer and duplication. This saves time and resources, allowing teams to focus on more creative and strategic tasks.
- Increased Accuracy: By leveraging the strengths of different software solutions, integrated workflows improve the overall accuracy and precision of project deliverables. This ensures that all project components are designed and constructed to the required standards.
Workflow Examples
Here are some real-world examples of how AutoCAD integrates with other Autodesk products to create efficient workflows:
- Architectural Design and Construction: An architect creates a 2D floor plan in AutoCAD and then imports it into Revit for BIM modeling. The architect can then share the BIM model with structural engineers, who can use Revit to design the building’s structure. The structural engineers can then export the structural elements back to AutoCAD for detailed drawings and documentation. This collaborative process ensures that all design elements are integrated and coordinated, leading to a successful construction project.
- Civil Engineering and Site Development: A civil engineer uses Civil 3D to create a site plan and design roads, utilities, and other infrastructure elements. The engineer can then export the design data to AutoCAD for further detailing and visualization. This process allows for the creation of comprehensive site plans and drawings that can be shared with contractors and other stakeholders.
Future Trends in AutoCAD
AutoCAD, a cornerstone of computer-aided design (CAD) software, has consistently evolved to meet the ever-changing demands of the design and engineering world. Looking ahead, several key trends and technologies will shape the future of AutoCAD, influencing how designers and engineers create, collaborate, and innovate.
Integration with Cloud Technologies
Cloud computing has revolutionized how we access and manage data, and AutoCAD is embracing this shift. Cloud-based platforms provide seamless collaboration, enabling real-time access to designs and project data from anywhere, anytime. This enhances team productivity, reduces storage requirements, and facilitates streamlined workflows.
Final Conclusion
As Autodesk AutoCAD continues to evolve, it remains a powerful tool for professionals seeking to push the boundaries of design and engineering. Its integration with other Autodesk products and its embrace of emerging technologies ensure that it remains at the forefront of the industry, empowering users to create, innovate, and shape the world around us.
Autodesk AutoCAD is a powerful design and drafting software, often used in conjunction with other productivity tools like windows office for creating presentations and reports. While AutoCAD focuses on technical drawings, Windows Office provides the tools for organizing and presenting those designs effectively.
