CATIA, short for Computer Aided Three-Dimensional Interactive Application, is a powerful and comprehensive software suite used in various industries for product design, engineering, and manufacturing. Developed by Dassault Systèmes, CATIA has become an industry standard, renowned for its advanced features, extensive capabilities, and ability to handle complex projects.
Table of Contents
CATIA offers a wide range of modules catering to different aspects of the product lifecycle, from conceptual design and 3D modeling to simulation, analysis, and manufacturing. Its user-friendly interface, intuitive workflows, and extensive customization options make it a valuable tool for engineers, designers, and manufacturers worldwide.
CATIA Overview
CATIA, an acronym for Computer Aided Three-Dimensional Interactive Application, is a powerful and comprehensive software suite used for product design, engineering, and manufacturing. Its purpose is to streamline and optimize the entire product lifecycle, from conceptualization and design to manufacturing and maintenance.
History of CATIA
CATIA’s development began in the 1970s at Dassault Aviation, a French aerospace company. Initially, it was intended to support the design and manufacturing of aircraft. As CATIA gained popularity and its capabilities expanded, it became a widely adopted software solution for various industries, including automotive, shipbuilding, and consumer goods.
CATIA’s evolution has been marked by significant advancements in its features and functionalities. Early versions focused on 3D modeling and surface design, while later versions incorporated capabilities like finite element analysis, simulation, and collaborative design. The software has continuously adapted to meet the evolving needs of its users, embracing advancements in computer technology and design methodologies.
Key Features and Capabilities: Catia
CATIA is a comprehensive CAD/CAM/CAE software suite renowned for its powerful features and capabilities, encompassing a wide range of applications across various industries. Its core functionalities cater to diverse needs, from product design and engineering to manufacturing and analysis.
3D Modeling
3D modeling is the foundation of CATIA, enabling users to create realistic and detailed representations of products and assemblies. It provides a wide array of tools for generating complex geometries, including:
- Solid Modeling: CATIA offers robust solid modeling capabilities, allowing users to create 3D objects with volume and mass properties. This is essential for accurate analysis and simulation.
- Surface Modeling: CATIA excels in surface modeling, enabling the creation of complex, free-form shapes that are often found in automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods design. This includes tools for generating curves, surfaces, and blends.
- Wireframe Modeling: While less common in modern design, CATIA also supports wireframe modeling, which uses lines and curves to define the basic shape of an object. This can be useful for creating initial sketches or for representing lightweight objects.
Design
Beyond 3D modeling, CATIA provides advanced design tools that facilitate the creation of functional and innovative products. Key features include:
- Parametric Design: CATIA leverages parametric design principles, allowing users to define relationships between design elements. This enables automatic updates and modifications, ensuring consistency and efficiency throughout the design process.
- Assembly Design: CATIA’s assembly design capabilities streamline the process of creating complex assemblies. Users can manage components, define constraints, and perform motion studies to analyze and optimize assemblies.
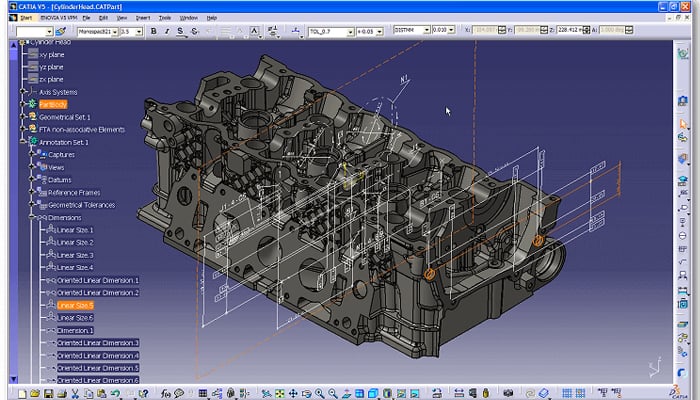
- Drafting and Detailing: CATIA integrates drafting and detailing functionalities, enabling users to create production drawings, technical specifications, and other documentation required for manufacturing and production.
Analysis
CATIA’s analysis capabilities enable engineers to evaluate product performance and optimize designs before physical prototypes are built. This includes:
- Finite Element Analysis (FEA): CATIA integrates FEA tools for simulating stress, strain, and other structural behaviors. This helps engineers identify potential weaknesses and optimize designs for strength and durability.
- Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD): CATIA provides CFD capabilities for analyzing fluid flow and heat transfer. This is essential for designing products such as aircraft, automobiles, and medical devices.
- Kinematic Analysis: CATIA’s kinematic analysis tools enable engineers to simulate the movement of mechanical systems. This helps in optimizing designs for motion, speed, and efficiency.
Manufacturing
CATIA’s manufacturing capabilities facilitate the creation of production plans and documentation, ensuring smooth and efficient production processes. Key features include:
- NC Programming: CATIA provides tools for generating NC programs, which control machine tools and robots. This allows for automated machining and fabrication of complex parts.
- Tooling Design: CATIA supports tooling design, enabling the creation of molds, dies, and other manufacturing tools. This ensures the efficient and accurate production of parts.
- Process Planning: CATIA integrates process planning functionalities, enabling users to define and optimize manufacturing sequences and operations. This ensures a smooth and efficient production workflow.
Modules and Applications
CATIA is structured into various modules, each tailored to specific industry needs and applications. These modules include:
- CATIA V5: This is the most widely used version of CATIA, offering a comprehensive suite of functionalities for various industries.
- CATIA V6 (3DEXPERIENCE): The latest version of CATIA, built on the 3DEXPERIENCE platform, provides a collaborative and cloud-based environment for design, engineering, and manufacturing.
- CATIA for Automotive: This module caters to the specific needs of the automotive industry, providing tools for vehicle design, engineering, and manufacturing.
- CATIA for Aerospace: This module is designed for the aerospace industry, offering functionalities for aircraft design, analysis, and manufacturing.
- CATIA for Shipbuilding: This module provides tools for designing, engineering, and manufacturing ships and marine structures.
Comparison with Other CAD/CAM Software
CATIA is a leading CAD/CAM software solution, competing with other popular programs like SolidWorks, Autodesk Inventor, and Siemens NX. While each software offers unique strengths, CATIA distinguishes itself through:
- Comprehensive Functionality: CATIA provides a comprehensive suite of features, covering design, analysis, manufacturing, and other related aspects. This makes it a powerful and versatile tool for various industries.
- Industry-Specific Modules: CATIA offers specialized modules for specific industries, such as automotive, aerospace, and shipbuilding. This ensures tailored functionalities and workflows for specific applications.
- Advanced Analysis Capabilities: CATIA excels in analysis, providing robust FEA, CFD, and kinematic analysis tools. This enables engineers to perform in-depth simulations and optimize designs.
- Integration with Other Dassault Systèmes Products: CATIA seamlessly integrates with other Dassault Systèmes products, such as DELMIA and SIMULIA, providing a comprehensive and integrated solution for product lifecycle management.
Industries and Applications
CATIA is a powerful and versatile software solution that finds applications in a wide range of industries. Its comprehensive capabilities cater to the unique requirements of diverse sectors, enabling businesses to optimize their design, engineering, and manufacturing processes.
Industries Utilizing CATIA
CATIA is widely used in various industries, including:
- Automotive
- Aerospace
- Shipbuilding
- Consumer Goods
- Industrial Equipment
- Energy
- Defense
- Medical Devices
- Electronics
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry relies heavily on CATIA for designing and engineering vehicles. Some key applications include:
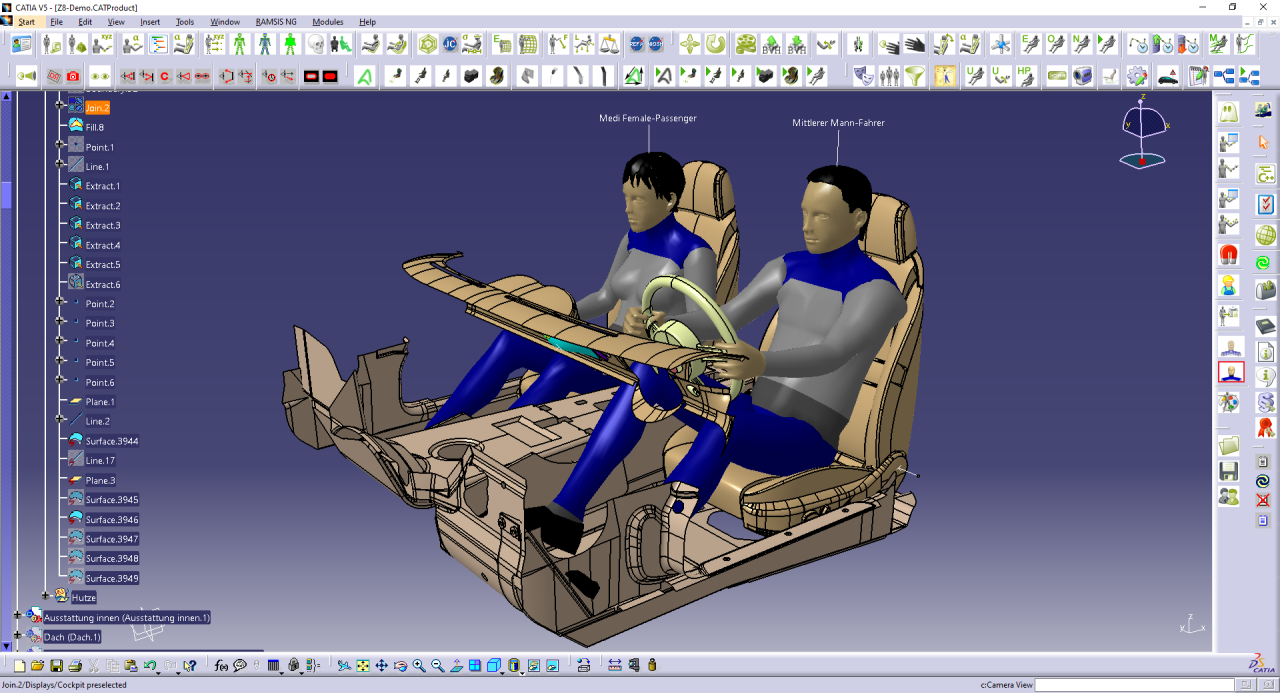
- Vehicle Body Design: CATIA facilitates the creation of complex vehicle body shapes, including surfaces, curves, and features, ensuring aerodynamic efficiency and aesthetic appeal.
- Chassis Design: The software assists in designing and simulating the chassis, suspension, and other critical components, optimizing performance and durability.
- Engine Design: CATIA enables engineers to design and analyze engine components, including combustion chambers, pistons, and connecting rods, for optimal power and fuel efficiency.
- Virtual Prototyping: CATIA allows for virtual prototyping of vehicles, enabling engineers to test and validate designs before physical production, reducing development time and costs.
The benefits of using CATIA in the automotive industry include:
- Improved Design Efficiency: CATIA streamlines the design process, allowing engineers to create and modify designs quickly and efficiently.
- Enhanced Collaboration: The software facilitates seamless collaboration between design teams, engineers, and manufacturing personnel.
- Reduced Development Time: Virtual prototyping and simulation capabilities significantly reduce the time required for product development.
- Cost Optimization: By identifying potential issues early in the design phase, CATIA helps reduce manufacturing costs and rework.
- Improved Product Quality: The software enables engineers to create highly detailed and accurate designs, leading to improved product quality and reliability.
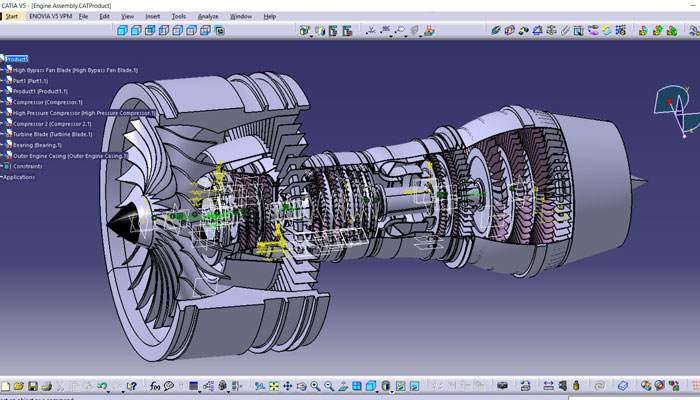
Aerospace Industry
CATIA is essential in the aerospace industry for designing and manufacturing aircraft, spacecraft, and other aerospace components. Here are some key applications:
- Aircraft Design: CATIA facilitates the design of aircraft fuselages, wings, tail sections, and other components, optimizing aerodynamic performance and structural integrity.
- Spacecraft Design: The software assists in designing and simulating spacecraft structures, propulsion systems, and payloads, ensuring functionality and safety.
- Engine Design: CATIA enables engineers to design and analyze jet engines, turbofan engines, and other propulsion systems for optimal performance and efficiency.
- Virtual Flight Testing: CATIA allows for virtual flight testing, enabling engineers to evaluate aircraft performance and stability before physical flight tests, reducing development costs and risks.
The benefits of using CATIA in the aerospace industry include:
- Improved Design Accuracy: CATIA provides a high level of design accuracy, ensuring precise component dimensions and tolerances, critical for aerospace applications.
- Enhanced Safety: The software’s simulation capabilities enable engineers to identify potential safety hazards and design solutions to mitigate them.
- Reduced Development Costs: Virtual prototyping and simulation reduce the need for physical prototypes, significantly lowering development costs.
- Faster Time to Market: CATIA streamlines the design and manufacturing processes, accelerating the time it takes to bring new aircraft and spacecraft to market.
- Increased Efficiency: The software’s comprehensive capabilities optimize design and manufacturing processes, improving overall efficiency.
Shipbuilding Industry
CATIA plays a vital role in the shipbuilding industry, supporting the design, engineering, and construction of ships, submarines, and other marine vessels. Key applications include:
- Hull Design: CATIA enables engineers to design complex hull shapes, optimizing hydrodynamics and structural integrity.
- Engine Room Design: The software assists in designing and simulating engine rooms, including propulsion systems, auxiliary machinery, and piping systems.
- Deck Layout: CATIA facilitates the design and arrangement of decks, superstructures, and other onboard features, ensuring functionality and passenger comfort.
- Virtual Shipyard: CATIA allows for the creation of virtual shipyards, enabling engineers to simulate the construction process and identify potential bottlenecks or issues.
The benefits of using CATIA in the shipbuilding industry include:
- Improved Design Quality: CATIA enables engineers to create highly detailed and accurate ship designs, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
- Reduced Construction Time: The software streamlines the design and construction processes, reducing the time it takes to build ships.
- Cost Optimization: By identifying potential issues early in the design phase, CATIA helps minimize construction costs and rework.
- Enhanced Collaboration: The software facilitates seamless collaboration between design teams, engineers, and shipyard personnel.
- Increased Efficiency: CATIA optimizes the shipbuilding process, improving overall efficiency and productivity.
Consumer Goods Industry
CATIA is widely used in the consumer goods industry for designing and manufacturing products such as appliances, electronics, furniture, and toys. Key applications include:
- Product Design: CATIA enables engineers to create aesthetically pleasing and functional product designs, considering ergonomics, usability, and manufacturability.
- Packaging Design: The software assists in designing and simulating packaging for consumer goods, ensuring product protection and brand appeal.
- Virtual Prototyping: CATIA allows for virtual prototyping of consumer goods, enabling engineers to test and validate designs before physical production, reducing development time and costs.
- Manufacturing Process Optimization: CATIA helps optimize manufacturing processes, ensuring efficient production and minimizing waste.
The benefits of using CATIA in the consumer goods industry include:
- Improved Product Design: CATIA enables engineers to create innovative and user-friendly product designs, meeting consumer demands and enhancing brand image.
- Reduced Development Time: Virtual prototyping and simulation accelerate the product development process, allowing for faster time to market.
- Cost Optimization: CATIA helps reduce manufacturing costs by optimizing designs and processes, minimizing waste and rework.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: By creating high-quality products that meet consumer expectations, CATIA contributes to increased customer satisfaction and brand loyalty.
- Increased Competitiveness: The software enables businesses to develop and manufacture innovative products more efficiently, enhancing their competitiveness in the market.
User Interface and Workflow
CATIA’s user interface is designed to be intuitive and efficient, enabling users to seamlessly navigate the software and access its various functionalities. The interface is organized around a central workspace, providing a comprehensive view of the design environment and tools.
CATIA User Interface Elements
The CATIA user interface is characterized by its well-defined elements, each playing a crucial role in facilitating the design process. Here are some of the key components:
- Toolbar: The toolbar provides quick access to commonly used tools and commands. It is typically located at the top of the screen, offering a convenient way to execute actions without navigating through menus.
- Command Bar: The command bar, located below the toolbar, displays the active command and its options, allowing users to fine-tune their actions. It also provides feedback on the current state of the design process.
- Tree View: The tree view, usually positioned on the left side of the screen, provides a hierarchical representation of the design elements. It allows users to navigate and manage the different parts, assemblies, and features of a model.
- Graphics Window: The graphics window, often the largest part of the interface, displays the 3D model. This is where users interact with the model, manipulating its geometry and applying various design features.
- Status Bar: The status bar, located at the bottom of the screen, provides information about the current status of the software, such as the selected tool, active command, and system resources.
CATIA Workflow: A Simple 3D Model Creation
The following steps Artikel a basic workflow for creating a simple 3D model in CATIA:
- Start CATIA: Launch the CATIA software and select the desired workspace. For basic modeling, the “Part Design” workspace is often used.
- Create a New Part: Click on the “New” button or use the “File” menu to create a new part file. This will open a blank canvas for your 3D model.
- Sketching: Use the sketching tools, accessible from the toolbar or the “Sketch” menu, to create a 2D profile. This profile will serve as the basis for your 3D model.
For example, you can sketch a rectangle or a circle.
- Extrusion: Select the sketched profile and use the “Extrude” command to create a 3D solid by extending the profile along a specific direction.
This will transform your 2D sketch into a 3D shape.
- Features: Add features to the 3D model, such as holes, fillets, or chamfers, using the tools available in the “Features” menu. These features enhance the functionality and aesthetics of your design.
- Save the Model: Once your design is complete, save the model using the “Save” button or the “File” menu. This will preserve your work for future access and modification.
Tools and Functions in CATIA
CATIA offers a comprehensive set of tools and functions that cater to various aspects of the design process. These tools can be broadly categorized into:
- Geometric Modeling: Tools for creating and manipulating 3D geometry, including sketching, extrusion, revolving, sweeping, and lofting.
- Surface Modeling: Tools for creating and manipulating complex surfaces, including ruled surfaces, offset surfaces, and blended surfaces.
- Assembly Modeling: Tools for assembling multiple parts into a complete product, including constraints, mates, and assemblies.
- Analysis and Simulation: Tools for analyzing the performance and behavior of a design, including finite element analysis (FEA), computational fluid dynamics (CFD), and kinematics.
- Drafting and Documentation: Tools for creating technical drawings and documentation, including views, sections, and annotations.
- Customization and Automation: Tools for customizing the user interface, creating macros, and automating repetitive tasks.
Advantages and Disadvantages
CATIA, a powerful and comprehensive 3D design and engineering software, offers a multitude of advantages that have made it a popular choice across various industries. However, it also presents certain disadvantages that potential users should consider before making a decision. This section delves into both the pros and cons of utilizing CATIA, providing a balanced perspective on its strengths and weaknesses.
Advantages of CATIA
The primary advantages of using CATIA stem from its advanced features, industry-standard compatibility, and comprehensive functionalities. These benefits contribute to improved design efficiency, enhanced product quality, and streamlined workflows.
- Advanced Features: CATIA boasts a wide array of advanced features that empower users to create complex designs, perform sophisticated simulations, and optimize product performance. These features include:
- Surface Modeling: CATIA’s powerful surface modeling capabilities allow users to create intricate and aesthetically pleasing designs, often used in automotive and aerospace industries where aerodynamic efficiency is paramount.
- Solid Modeling: Solid modeling in CATIA enables users to create 3D representations of objects with precise dimensions and properties, facilitating detailed analysis and virtual prototyping.
- Finite Element Analysis (FEA): CATIA’s FEA capabilities allow users to simulate the behavior of products under various conditions, ensuring structural integrity and optimizing design for performance.
- Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD): CFD simulations in CATIA enable users to analyze fluid flow and heat transfer, crucial for designing efficient and aerodynamic products.
- Industry-Standard Compatibility: CATIA’s compatibility with industry-standard file formats, such as IGES, STEP, and STL, ensures seamless data exchange between different design and manufacturing software applications. This interoperability promotes collaboration and reduces the risk of data loss or incompatibility issues.
- Comprehensive Functionalities: CATIA offers a comprehensive suite of functionalities that cover the entire product development lifecycle, from concept design to manufacturing and maintenance. This integrated approach streamlines workflows and eliminates the need for multiple software applications, saving time and resources.
Disadvantages of CATIA
While CATIA offers significant advantages, it also comes with certain disadvantages that potential users should be aware of. These drawbacks primarily relate to the software’s complexity, learning curve, and licensing costs.
- Complexity: CATIA is a highly complex software with a vast array of features and functionalities. This complexity can make it challenging for new users to learn and master the software, requiring significant time and effort to become proficient.
- Learning Curve: The steep learning curve associated with CATIA can be a significant barrier for new users. Mastering the software’s advanced features and functionalities requires extensive training and practice, potentially delaying project timelines and increasing development costs.
- Licensing Costs: CATIA’s licensing costs can be substantial, particularly for large organizations with multiple users. These costs can include software licenses, maintenance fees, and training expenses, adding to the overall project budget.
Learning Resources and Support
Mastering CATIA requires dedicated learning and ongoing support. Fortunately, numerous resources are available to help you navigate the software’s complexities and enhance your skills.
Online Learning Resources
Numerous online resources offer comprehensive CATIA learning experiences, from beginner-friendly tutorials to advanced training programs.
- Dassault Systèmes’ Official Website: The official CATIA website provides a wealth of resources, including tutorials, documentation, and training materials. You can access user guides, technical specifications, and interactive simulations to deepen your understanding of CATIA’s functionalities.
- Online Learning Platforms: Platforms like Udemy, Coursera, and Skillshare offer a wide range of CATIA courses taught by experienced instructors. These platforms provide structured learning paths, interactive exercises, and certification opportunities.
- YouTube Tutorials: YouTube is a treasure trove of CATIA tutorials, covering various aspects of the software, from basic modeling techniques to advanced simulations. Many creators provide step-by-step guides, practical examples, and troubleshooting tips.
- Online Forums and Communities: Forums like the CATIA Community on Dassault Systèmes’ website and other dedicated forums provide a platform for users to connect, share knowledge, and seek assistance from experienced professionals.
CATIA Certification Programs
CATIA certification programs validate your skills and expertise in using the software.
- Benefits of Certification: CATIA certification demonstrates your proficiency in the software, enhancing your credibility in the job market. It also provides a structured learning path, allowing you to acquire in-depth knowledge and practical skills.
- Types of Certifications: Dassault Systèmes offers various CATIA certification programs, tailored to specific industries and skill levels. These certifications cover areas like mechanical design, surface design, and product lifecycle management.
- Preparation Resources: To prepare for CATIA certification exams, you can access official study materials, practice tests, and online training programs.
Technical Support Options
CATIA users have access to various technical support options to address challenges and resolve issues.
- Dassault Systèmes Support: Dassault Systèmes offers comprehensive technical support through its dedicated support channels. This includes online resources, phone support, and email assistance.
- Community Forums: Online forums and communities provide a platform for users to connect, share knowledge, and seek assistance from experienced professionals.
- Third-Party Support Providers: Several third-party support providers offer specialized technical support services for CATIA users. These providers often have deep expertise in specific areas of the software, enabling them to provide tailored solutions.
Future Trends and Developments
The CAD/CAM landscape is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and changing industry demands. These trends are shaping the future of CATIA, leading to new capabilities and enhanced user experiences.
AI Integration
AI is revolutionizing the way products are designed and manufactured. CATIA is incorporating AI to enhance its capabilities, automating tasks, improving design accuracy, and providing valuable insights.
- Generative Design: AI algorithms can generate multiple design options based on user-defined constraints, optimizing for performance, weight, and cost. This empowers engineers to explore a wider range of possibilities and find innovative solutions.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI can analyze sensor data from machines and predict potential failures, enabling proactive maintenance and reducing downtime. CATIA can integrate with these systems to provide real-time insights and optimize production processes.
- Automated Design Optimization: AI can analyze vast datasets of design parameters and manufacturing processes to identify optimal configurations. This can significantly reduce design cycles and improve product quality.
Cloud-Based Platforms
Cloud computing is transforming the way software is accessed and utilized. CATIA is embracing cloud platforms to offer greater scalability, flexibility, and accessibility.
- Collaboration and Data Sharing: Cloud platforms enable seamless collaboration between teams, allowing them to access and share design data in real-time, regardless of location. This fosters better communication and improves efficiency.
- On-Demand Resources: Cloud-based CATIA provides access to powerful computing resources on demand, eliminating the need for expensive hardware investments. This allows users to scale their operations based on their needs and budget.
- Increased Accessibility: Cloud platforms make CATIA accessible from any device with an internet connection, empowering users to work from anywhere, anytime. This promotes remote work and increases flexibility.
Virtual Reality Applications
VR is emerging as a powerful tool for product visualization, design review, and training. CATIA is incorporating VR technologies to create immersive experiences that enhance collaboration and understanding.
- Interactive Design Review: VR allows users to interact with 3D models in a virtual environment, enabling more effective design reviews and identifying potential issues early in the development process.
- Enhanced Training: VR simulations provide realistic and interactive training environments for engineers and operators, allowing them to learn new skills and processes in a safe and controlled setting.
- Product Visualization: VR enables customers to experience products before they are built, providing a more engaging and interactive way to showcase design features and functionality.
Case Studies and Success Stories
CATIA’s impact extends beyond its features; real-world applications demonstrate its effectiveness in diverse industries. Examining successful implementations showcases how CATIA drives innovation and efficiency.
Automotive Industry: The Evolution of Car Design
The automotive industry heavily relies on CATIA for its intricate design processes. Here’s how CATIA has helped automotive manufacturers achieve remarkable results:
- Porsche: Porsche used CATIA to develop the 911 GT3 RS, a high-performance sports car. CATIA’s advanced surfacing capabilities allowed Porsche to create complex and aerodynamically efficient bodywork, contributing to the car’s exceptional performance.
- Tesla: Tesla, known for its electric vehicles, utilizes CATIA for designing and engineering its vehicles. CATIA’s ability to handle complex geometries and integrate different engineering disciplines enables Tesla to develop innovative and technologically advanced cars.
- Ford: Ford leverages CATIA to streamline its design and manufacturing processes. CATIA’s digital mock-up capabilities allow Ford to visualize and analyze vehicle designs virtually, reducing the need for physical prototypes and accelerating development cycles.
Aerospace Industry: Taking Flight with CATIA
The aerospace industry demands precision and efficiency. CATIA plays a crucial role in aircraft design and development:
- Airbus: Airbus, a leading aircraft manufacturer, employs CATIA for designing and developing its aircraft. CATIA’s advanced modeling and simulation capabilities allow Airbus to create complex aircraft structures, optimize aerodynamic performance, and ensure structural integrity.
- Boeing: Boeing, another major aircraft manufacturer, uses CATIA for designing and engineering its aircraft. CATIA’s comprehensive suite of tools enables Boeing to manage complex design data, collaborate with suppliers, and ensure the quality and reliability of its aircraft.
- SpaceX: SpaceX, known for its ambitious space exploration projects, leverages CATIA for designing and building its rockets and spacecraft. CATIA’s advanced modeling and simulation capabilities allow SpaceX to create complex structures, analyze performance, and optimize design for spaceflight.
Consumer Goods Industry: Designing for Everyday Life
CATIA’s versatility extends to the consumer goods industry, where it helps create products that we use daily:
- Apple: Apple, known for its sleek and innovative products, uses CATIA to design its consumer electronics. CATIA’s advanced surfacing and modeling capabilities enable Apple to create aesthetically pleasing and functional products.
- Samsung: Samsung, a leading manufacturer of smartphones and other consumer electronics, utilizes CATIA for product design and development. CATIA’s comprehensive tools allow Samsung to create complex designs, simulate product performance, and manage manufacturing processes efficiently.
- Nike: Nike, a global sportswear giant, employs CATIA for designing and developing its footwear and apparel. CATIA’s advanced modeling and simulation capabilities enable Nike to create innovative and functional products that meet the needs of athletes and consumers.
Comparison with Other Software
CATIA, a powerful and versatile CAD/CAM software, is widely used in various industries. However, it is not the only option available. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of CATIA in comparison to other popular CAD/CAM software can help you make an informed decision for your specific needs.
Comparison Table
This table provides a concise overview of CATIA’s key features and capabilities in comparison to SolidWorks, Autodesk Inventor, and Siemens NX.
| Feature | CATIA | SolidWorks | Autodesk Inventor | Siemens NX |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Industries | Aerospace, Automotive, Manufacturing, Consumer Products | Mechanical engineering, product design, manufacturing | Mechanical engineering, product design, manufacturing | Aerospace, Automotive, Industrial Machinery, Energy |
| Key Features | Advanced surfacing, complex assemblies, product lifecycle management (PLM) integration | Ease of use, parametric modeling, strong assembly capabilities | Strong design automation features, good for collaborative design | Comprehensive toolset for complex designs, advanced simulation capabilities |
| Capabilities | Complex geometry, multi-body assemblies, simulation, data management | Solid modeling, surface modeling, sheet metal design, rendering | Solid modeling, surface modeling, assembly design, simulation | Solid modeling, surface modeling, advanced machining, CAM integration |
| Pricing | Subscription-based, various pricing tiers depending on features and modules | Subscription-based, various pricing tiers depending on features and modules | Subscription-based, various pricing tiers depending on features and modules | Subscription-based, various pricing tiers depending on features and modules |
Target Industries
CATIA is widely used in industries requiring complex design and manufacturing processes. It excels in areas like aerospace, automotive, and shipbuilding, where high precision and intricate geometries are crucial. SolidWorks, on the other hand, is popular in mechanical engineering, product design, and manufacturing. It is known for its user-friendly interface and ease of use, making it suitable for a broader range of applications. Autodesk Inventor is also geared towards mechanical engineering and product design, with a focus on design automation and collaborative design workflows. Siemens NX, like CATIA, is widely used in industries like aerospace, automotive, and industrial machinery. It offers a comprehensive toolset for complex designs, advanced simulation capabilities, and strong CAM integration.
Key Features and Capabilities
CATIA’s strengths lie in its advanced surfacing capabilities, allowing for the creation of highly complex and intricate geometries. It also excels in managing complex assemblies and integrating product lifecycle management (PLM) systems. SolidWorks is known for its ease of use and parametric modeling capabilities, making it a popular choice for designers and engineers seeking a user-friendly platform. Autodesk Inventor emphasizes design automation features, enabling users to streamline design processes and collaborate effectively. Siemens NX stands out with its comprehensive toolset for complex designs, including advanced simulation capabilities and strong CAM integration.
Pricing
All four software solutions are available on a subscription-based model, with various pricing tiers depending on the features and modules included. The pricing structure for each software varies, and it’s recommended to contact the respective vendors for detailed pricing information.
Integration with Other Systems
CATIA’s strength lies not only in its powerful modeling capabilities but also in its seamless integration with other software and systems, creating a robust and efficient design and manufacturing ecosystem. This integration enables a smooth flow of data and processes, minimizing errors, optimizing workflows, and ultimately enhancing product development from concept to production.
Integration with PLM Systems
CATIA’s integration with Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) systems is a key factor in its success. PLM systems act as a central repository for product data, managing all aspects of a product’s lifecycle, from design and engineering to manufacturing, marketing, and even product retirement. This integration allows for:
- Data sharing and collaboration: Engineers, designers, and other stakeholders can access and share the same product data, eliminating inconsistencies and ensuring everyone is working on the latest version.
- Version control and change management: PLM systems track all changes made to the product design, providing a clear history of revisions and ensuring that only approved changes are implemented.
- Centralized data management: PLM systems provide a single source of truth for product data, eliminating the need for multiple versions of the same information and reducing the risk of errors.
For example, a company using CATIA and a PLM system can track the progress of a new product design, manage changes to the design, and ensure that all stakeholders have access to the latest version of the product data.
Integration with CAM Systems
CATIA integrates with Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) systems, enabling a direct transfer of design data to manufacturing processes. This integration streamlines the transition from design to production, reducing the potential for errors and delays. Some benefits include:
- Direct data transfer: Design data from CATIA can be automatically transferred to CAM systems, eliminating the need for manual data entry and reducing the risk of errors.
- Optimized toolpaths: CAM systems can utilize CATIA’s design data to generate optimized toolpaths for CNC machines, leading to faster and more efficient machining processes.
- Improved manufacturing accuracy: The integration ensures that the manufacturing process adheres to the precise specifications defined in the CATIA design, minimizing deviations and improving product quality.
For instance, a company can use CATIA to design a complex mold for a plastic part, then directly transfer the design data to a CAM system to generate the toolpaths for a CNC machine that will manufacture the mold.
Integration with Simulation Tools
CATIA integrates with simulation tools, allowing engineers to analyze and optimize designs before they are physically manufactured. This integration enables:
- Virtual prototyping: Engineers can create virtual prototypes of their designs and test them under various conditions, such as stress, vibration, and heat, without the need for physical prototypes.
- Early problem detection: Simulation tools can identify potential problems in a design before it is manufactured, saving time and resources by avoiding costly rework later in the process.
- Improved design performance: Simulation results can be used to optimize the design, improving its performance, efficiency, and durability.
For example, a company can use CATIA to design a car chassis, then integrate it with a simulation tool to analyze the chassis’s structural integrity under different loading conditions. The results of the simulation can then be used to improve the chassis’s design and ensure it can withstand the stresses of real-world driving conditions.
Best Practices and Tips
Mastering CATIA involves more than just learning its features; it’s about adopting efficient practices and techniques to maximize its potential. This section explores best practices and tips to streamline your workflow, improve performance, and achieve desired results.
Organizing Your Work
Organizing your work effectively is crucial for efficient design and analysis in CATIA. A well-structured project not only ensures clarity but also facilitates collaboration and error prevention.
- Establish a clear project structure: Create a hierarchical folder system for your CATIA projects. This makes it easier to find specific files, manage versions, and collaborate with others.
- Use meaningful names: Give your files, folders, and parts descriptive names that reflect their content. This avoids confusion and helps you quickly locate the necessary elements.
- Utilize layers: Organize your design elements into layers to control visibility and manage complexity. This allows you to focus on specific parts of the model without cluttering the workspace.
- Employ templates: Create templates for frequently used configurations, such as standard parts or drawing layouts. This saves time and ensures consistency across projects.
Optimizing CATIA Performance
CATIA is a powerful software, but its performance can be affected by factors like model complexity, system resources, and user habits. By optimizing your workflow, you can significantly improve responsiveness and reduce processing time.
- Simplify geometry: Avoid unnecessary complexity in your models. Use simpler shapes and features whenever possible to reduce the computational load on CATIA.
- Utilize lightweight features: Explore CATIA’s lightweight features, such as lightweight surfaces and bodies, to reduce file size and improve performance. These features offer a simplified representation of geometry, ideal for visualization and analysis.
- Manage data size: Keep your models and files manageable by periodically cleaning up unused data and consolidating similar elements.
- Optimize graphics settings: Adjust your graphics settings based on your hardware capabilities and project requirements. This can significantly impact performance, especially when working with complex models.
- Utilize CATIA’s performance tools: CATIA offers built-in tools for analyzing performance bottlenecks and optimizing settings. Leverage these tools to identify and address performance issues effectively.
Enhancing Modeling Techniques
CATIA provides a wide range of modeling tools and techniques. By mastering these techniques, you can create efficient, accurate, and visually appealing designs.
- Utilize parametric modeling: Take advantage of CATIA’s parametric modeling capabilities to define relationships between design elements. This allows you to easily modify your design by changing parameters, ensuring consistency and reducing errors.
- Explore advanced features: Familiarize yourself with advanced features like surfacing, assembly modeling, and knowledge-based engineering. These tools can significantly enhance your design process and improve the quality of your work.
- Leverage constraints: Employ constraints to define relationships between geometric entities. Constraints ensure that your model behaves as intended and helps prevent errors during modifications.
- Employ sketching techniques: Develop strong sketching skills. Accurate and well-defined sketches are the foundation for successful 3D modeling in CATIA.
Effective Collaboration
Collaboration is essential in many engineering projects. CATIA provides tools to facilitate seamless teamwork and knowledge sharing.
- Utilize version control: Implement a version control system to track changes and manage different iterations of your designs. This ensures a clear history of modifications and promotes collaboration without overwriting each other’s work.
- Employ CATIA’s collaboration tools: CATIA offers features for collaborative design, such as shared workspaces and collaborative design reviews. Leverage these tools to facilitate teamwork and knowledge sharing.
- Establish clear communication: Maintain open and consistent communication with your team members to ensure everyone is on the same page and to avoid misunderstandings. This can be achieved through regular meetings, documentation, and clear task assignments.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, CATIA plays a crucial role in the modern engineering and manufacturing landscape. Its ability to streamline design processes, enhance collaboration, and optimize product development makes it an invaluable asset for organizations across diverse industries. As technology continues to evolve, CATIA is poised to further revolutionize the way we design, engineer, and manufacture products, leading to greater efficiency, innovation, and competitiveness.
CATIA is a powerful software used in various industries for product design and engineering. However, even with its advanced features, accidental file deletion or system crashes can happen, leading to the loss of valuable data. Thankfully, you can recover lost CATIA files with the help of free data recovery software , which can scan your hard drive and potentially restore deleted files.
Once your CATIA files are recovered, you can continue working on your projects without losing valuable time and effort.
