MicroStation, a powerful and versatile Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software, has been a mainstay in the engineering and design industries for decades. Its robust capabilities, encompassing design, drafting, modeling, and visualization, have empowered professionals across diverse fields to create and manage complex projects with unparalleled precision and efficiency.
Table of Contents
From its humble beginnings, MicroStation has undergone significant evolution, constantly adapting to meet the ever-changing demands of the modern design landscape. Its user-friendly interface, combined with a rich array of features, has made it a preferred choice for professionals seeking a comprehensive and intuitive CAD solution.
MicroStation Overview
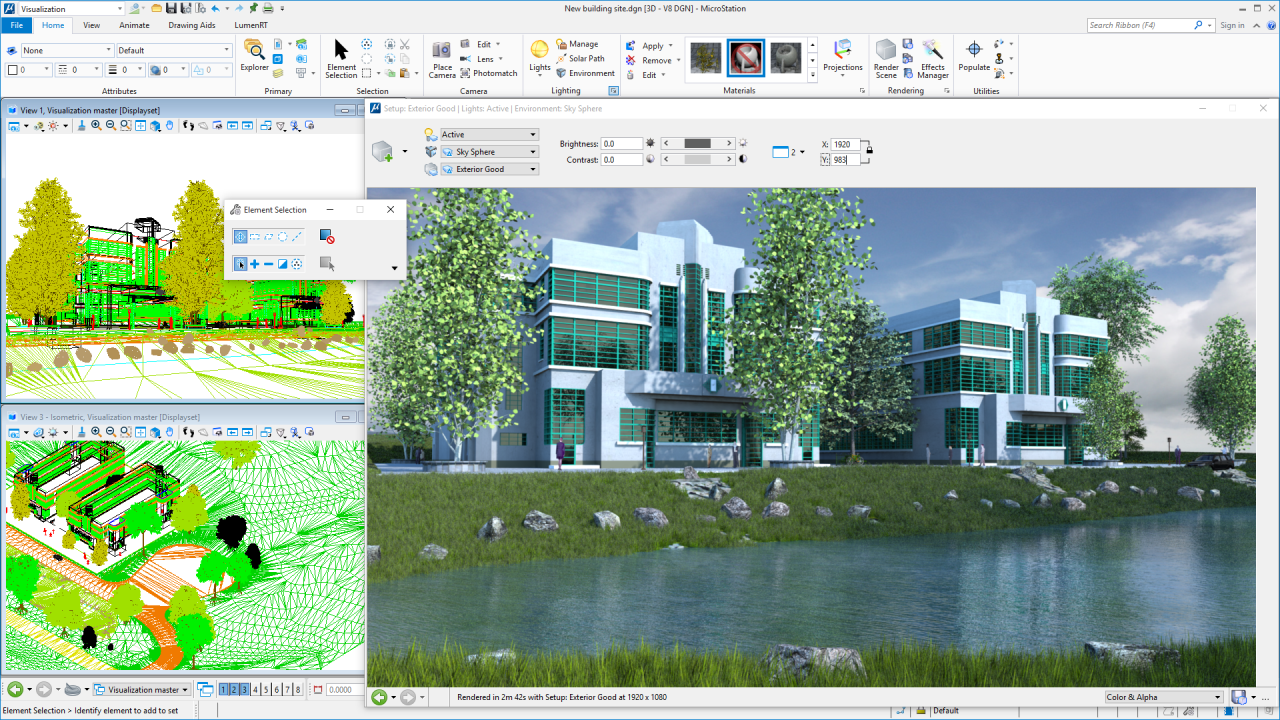
MicroStation is a powerful and versatile CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software widely used in various industries for creating, editing, and managing complex designs. It is known for its robust features, user-friendly interface, and ability to handle large and intricate projects.
History and Evolution
MicroStation’s journey began in the early 1980s, developed by Bentley Systems. Initially, it was a 2D drafting software, primarily used for architectural and engineering projects. Over the years, it has undergone significant evolution, incorporating advanced features like 3D modeling, visualization, and data management. MicroStation has adapted to the evolving technological landscape, integrating with other software applications and embracing industry standards.
User Interface
MicroStation’s user interface is designed to be intuitive and efficient. The software utilizes a ribbon-based interface, with a well-organized menu system that provides easy access to various tools and functions. The workspace is customizable, allowing users to arrange toolbars and palettes according to their preferences.
- The ribbon interface organizes tools and commands into logical groups, making it easy to find the necessary functionality.
- The workspace can be tailored to specific tasks or projects, providing a customized environment for different users.
- The software offers a comprehensive help system, providing documentation and tutorials to assist users in learning and using the software effectively.
Key Features of MicroStation
MicroStation is a powerful and versatile CAD software renowned for its comprehensive features and capabilities, designed to meet the diverse needs of engineers, architects, and designers across various industries. Its robust set of tools empowers users to create, edit, and manage complex designs with precision and efficiency.
Design and Drafting Capabilities
MicroStation offers a wide range of tools specifically tailored for design and drafting tasks, enabling users to create detailed and accurate drawings.
- Drawing Creation and Editing: MicroStation provides a comprehensive set of tools for creating and editing various types of drawings, including 2D and 3D models, schematics, and plans. Users can draw lines, arcs, circles, and other geometric shapes, as well as text and annotations.
- Dimensioning and Annotation: Accurate dimensioning and annotation are crucial for effective communication in design and engineering. MicroStation provides tools for creating and managing dimensions, text, and other annotations, ensuring clear and precise documentation of designs.
- Layer Management: MicroStation’s robust layer management system allows users to organize and manage different elements of a drawing efficiently. Layers can be used to group related objects, control visibility, and apply specific properties to different parts of the design.
- Symbol Libraries: MicroStation includes extensive symbol libraries, offering a wide range of pre-defined symbols and components for various industries. These libraries simplify the design process by providing readily available elements, saving time and effort.
- Design Standards and Templates: MicroStation supports industry-specific design standards and templates, ensuring consistency and compliance with regulations. Users can create and use custom templates to streamline the design process and maintain a uniform design style.
Advanced Modeling and Visualization
MicroStation’s advanced modeling and visualization capabilities allow users to create and explore complex designs in a comprehensive and interactive manner.
- 3D Modeling: MicroStation offers a powerful 3D modeling environment, enabling users to create and manipulate complex 3D models. It supports various modeling techniques, including solid modeling, surface modeling, and parametric modeling, providing flexibility and accuracy in creating intricate designs.
- Realistic Rendering: MicroStation provides advanced rendering capabilities, allowing users to create photorealistic images of their designs. It supports various rendering techniques, including ray tracing, global illumination, and material mapping, resulting in high-quality visualizations that accurately represent the final design.
- Visualizations and Animations: MicroStation’s visualization tools allow users to create interactive 3D models, animations, and walkthroughs. These features enable users to explore and present their designs in a dynamic and engaging way, enhancing communication and collaboration.
- Data Visualization: MicroStation’s data visualization capabilities allow users to integrate and visualize data from various sources, such as spreadsheets, databases, and GIS systems. This feature enables users to gain insights from data and make informed design decisions based on real-time information.
MicroStation Applications
MicroStation’s versatility extends across a wide range of industries, making it a valuable tool for various engineering disciplines. This section explores the diverse applications of MicroStation in different sectors, showcasing its ability to address complex engineering challenges.
Applications Across Industries
MicroStation’s applications are vast, encompassing numerous industries, each with unique requirements and challenges. The following table provides a concise overview of the industries where MicroStation is widely used:
| Industry | Applications |
|---|---|
| Civil Engineering | Road and highway design, bridge design, drainage systems, water and wastewater treatment plants, land development, surveying, and GIS. |
| Architectural Engineering | Building information modeling (BIM), architectural design, structural engineering, MEP (mechanical, electrical, and plumbing) design, and landscape architecture. |
| Mechanical Engineering | Plant design, equipment layout, piping and instrumentation diagrams (P&IDs), and product design. |
| Electrical Engineering | Power distribution systems, substation design, and electrical network modeling. |
| Geospatial Engineering | Geographic information systems (GIS), surveying, mapping, and remote sensing. |
| Manufacturing | Product design, factory layout, and manufacturing process planning. |
| Transportation | Railroad design, airport design, and transit systems. |
| Energy | Power plant design, oil and gas pipeline design, and renewable energy projects. |
Specific Applications in Engineering Disciplines
MicroStation’s application in engineering disciplines is multifaceted, encompassing various aspects of design, analysis, and construction. Here are some examples of how MicroStation is used in different engineering fields:
- Civil Engineering: MicroStation is extensively used for road and highway design, including alignment, grading, and pavement design. It is also used for bridge design, where engineers can model the complex geometry of bridges and analyze their structural behavior. Furthermore, MicroStation assists in the design of drainage systems, ensuring efficient water flow and preventing flooding.
- Architectural Engineering: In architectural engineering, MicroStation plays a vital role in building information modeling (BIM), enabling architects and engineers to create detailed 3D models of buildings. This facilitates collaboration, visualization, and analysis throughout the design and construction process. MicroStation is also used for structural engineering, allowing engineers to analyze the structural integrity of buildings and design load-bearing elements.
- Mechanical Engineering: MicroStation is used in mechanical engineering for plant design, including equipment layout, piping and instrumentation diagrams (P&IDs), and process flow diagrams. It also facilitates product design, allowing engineers to create detailed 3D models of components and assemblies.
- Electrical Engineering: In electrical engineering, MicroStation is used for power distribution systems, substation design, and electrical network modeling. Engineers can use MicroStation to create schematics, diagrams, and 3D models of electrical systems, ensuring efficient and reliable power distribution.
MicroStation Workflows
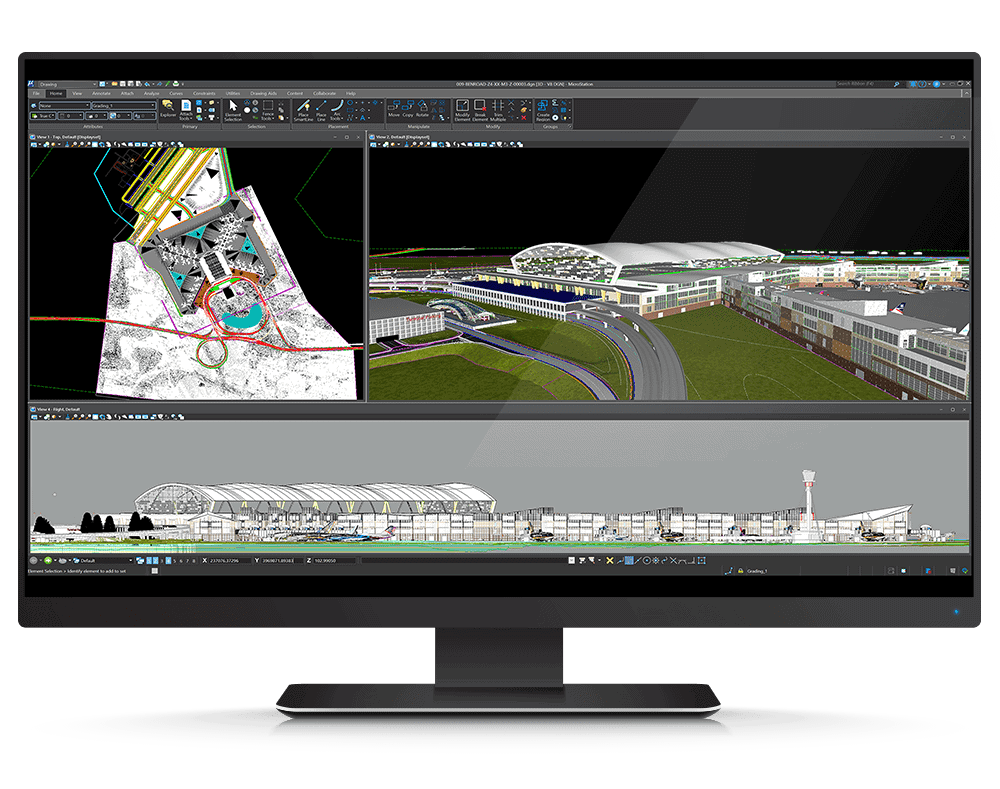
MicroStation workflows encompass the various steps and processes involved in utilizing the software for design, engineering, and construction projects. These workflows are often tailored to specific project requirements, but a general understanding of the common steps involved provides a solid foundation for efficient and effective use of MicroStation.
Typical Steps in a MicroStation Project
A typical MicroStation project workflow involves a sequence of steps, each contributing to the overall project completion. These steps can be broadly categorized as follows:
- Project Setup and Configuration: This initial stage involves creating a new project file, defining project settings, and establishing the necessary coordinate systems and units. It also includes importing existing data, such as survey data or CAD drawings, and configuring the workspace for efficient project management.
- Design and Modeling: The core of the project involves utilizing MicroStation’s tools to create and modify geometric objects, such as lines, curves, surfaces, and solids. This stage leverages the software’s capabilities for 2D and 3D modeling, drafting, and design visualization.
- Analysis and Simulation: MicroStation allows for integrating analysis and simulation tools, enabling engineers to perform structural analysis, hydraulic simulations, and other calculations directly within the design environment. This integration streamlines the design process and facilitates informed decision-making.
- Collaboration and Sharing: MicroStation promotes collaboration by enabling users to share project files, work on the same design concurrently, and access real-time updates. This collaborative environment enhances communication and ensures that all stakeholders are working with the most up-to-date information.
- Documentation and Output: The final stage involves generating project documentation, including drawings, reports, and other deliverables. MicroStation offers a wide range of output options, allowing users to create high-quality visuals, generate reports, and export data in various formats.
Role of MicroStation in Collaborative Design and Engineering Projects
MicroStation plays a crucial role in collaborative design and engineering projects by facilitating seamless information exchange and coordinated efforts among different stakeholders.
- Centralized Data Repository: MicroStation serves as a central repository for project data, ensuring that all team members have access to the latest design information. This centralized approach eliminates data silos and ensures consistency across the project.
- Version Control and Tracking: MicroStation’s version control capabilities allow for tracking changes made to the project data, providing a clear history of design revisions and facilitating efficient collaboration. This feature ensures that all stakeholders are aware of the latest updates and can easily revert to previous versions if needed.
- Real-Time Collaboration: MicroStation supports real-time collaboration, enabling multiple users to work on the same project simultaneously. This feature fosters a dynamic and efficient design process, allowing team members to contribute their expertise and receive immediate feedback.
- Integration with Other Software: MicroStation seamlessly integrates with other industry-standard software applications, such as BIM software and analysis tools. This interoperability allows for a smooth exchange of data between different software environments, enhancing collaboration and streamlining workflows.
Best Practices for Utilizing MicroStation Effectively
Maximizing the benefits of MicroStation requires adopting effective practices and strategies.
- Establish Clear Project Goals and Scope: Before starting a project, define the project objectives, scope, and deliverables to ensure a clear understanding of the requirements and expectations. This clarity will guide the design process and facilitate efficient workflow management.
- Optimize Project Settings and Configuration: Configure MicroStation settings and preferences to align with project requirements and user preferences. This optimization ensures that the software operates efficiently and effectively for the specific project needs.
- Utilize Templates and Standards: Leverage pre-defined templates and standards to maintain consistency and efficiency in the design process. This approach ensures that all project elements adhere to established guidelines and reduces the risk of errors.
- Adopt a Structured Approach: Organize project files and data in a logical and hierarchical manner to facilitate efficient navigation and management. This structured approach enhances collaboration and ensures that project information is readily accessible.
- Regularly Backup Project Data: Implement a robust data backup strategy to protect against data loss or corruption. Regular backups ensure that project data is safe and can be easily restored in case of unexpected events.
- Stay Updated with Software Enhancements: Regularly update MicroStation to benefit from the latest features, bug fixes, and performance enhancements. Staying up-to-date ensures that you are leveraging the full potential of the software and maximizing its benefits.
MicroStation Integration
MicroStation is designed to work seamlessly within a broader ecosystem of Bentley software and other industry-standard applications, enhancing collaboration and data exchange.
Integration with Other Bentley Products
MicroStation’s integration with other Bentley products fosters a unified workflow across various disciplines, enabling seamless data exchange and project coordination.
- ProjectWise: ProjectWise is Bentley’s collaborative platform for managing project information. It integrates with MicroStation, allowing users to share and manage project data, including drawings, models, and documentation, in a centralized repository. This facilitates real-time collaboration among project teams, reduces data duplication, and enhances project visibility.
- OpenBuildings Designer: OpenBuildings Designer is a comprehensive BIM software for architectural design. MicroStation’s integration with OpenBuildings Designer allows architects to leverage MicroStation’s powerful drafting and design capabilities while seamlessly sharing and coordinating design data with other BIM stakeholders. This streamlined workflow ensures consistent data across the project lifecycle.
- OpenRoads Designer: OpenRoads Designer is a civil engineering software for roadway design. MicroStation’s integration with OpenRoads Designer enables civil engineers to utilize MicroStation’s advanced modeling and visualization tools for roadway design and analysis, while seamlessly exchanging data with other disciplines involved in the project. This interoperability streamlines the design process and ensures data consistency.
- Bentley Navigator: Bentley Navigator is a visualization and review tool that provides a platform for accessing and reviewing project data from various Bentley applications. MicroStation’s integration with Bentley Navigator allows users to easily access and review project data, including models, drawings, and documentation, in a single platform. This facilitates informed decision-making and collaboration among stakeholders.
Interoperability with Other Software Applications
MicroStation supports industry-standard file formats and data exchange protocols, enabling seamless interoperability with other software applications, including:
- AutoCAD: MicroStation can import and export AutoCAD drawings (DWG/DXF) in various versions, ensuring compatibility with widely used CAD software. This facilitates data exchange with external partners and allows users to leverage existing AutoCAD drawings in MicroStation projects.
- Revit: MicroStation can import and export Revit models (RVT), enabling collaboration between architects and engineers using different BIM software. This interoperability streamlines the design process and ensures data consistency between architectural and structural models.
- IFC: MicroStation supports the Industry Foundation Classes (IFC) standard, a widely adopted format for exchanging BIM data. This enables seamless data exchange with other BIM software applications, regardless of the platform, fostering interoperability and collaboration across the industry.
- GIS: MicroStation can import and export geospatial data formats, such as shapefiles (SHP) and geodatabases (GDB), facilitating integration with Geographic Information Systems (GIS) software. This enables users to incorporate geographic context into their projects, enhancing spatial analysis and decision-making.
MicroStation Integration with BIM Workflows
MicroStation plays a vital role in BIM workflows, facilitating data exchange, collaboration, and visualization across different disciplines.
- Model Coordination: MicroStation’s integration with BIM software allows for model coordination between different disciplines, such as architecture, engineering, and construction. This ensures that all project components are designed and constructed according to the latest design data, minimizing clashes and rework.
- Visualization and Analysis: MicroStation’s powerful visualization and analysis tools allow users to create high-quality renderings and animations, enabling stakeholders to understand and review the design intent in detail. This facilitates informed decision-making and communication throughout the project lifecycle.
- Data Management: MicroStation’s integration with ProjectWise provides a centralized platform for managing project data, including BIM models, drawings, and documentation. This ensures data consistency, accessibility, and security, enhancing collaboration and streamlining the design process.
MicroStation Data Management
MicroStation is a powerful software that not only enables the creation of high-quality designs but also plays a crucial role in managing the vast amount of data associated with projects. It offers a robust data management system that ensures the integrity, accessibility, and collaboration of project information.
Project Data Handling, Microstation
MicroStation effectively manages project data by organizing it into a hierarchical structure. The core of this system is the drawing file, which serves as the central repository for all design elements, including geometry, attributes, and annotations. Drawing files are the primary units of data management in MicroStation.
- Drawing files are organized into a hierarchy of folders and subfolders, allowing for logical grouping of related designs.
- MicroStation allows for the creation of multiple drawing files within a project, facilitating the division of complex designs into manageable components.
- Each drawing file can contain various types of data, including geometry, text, images, and even external references to other files.
- The hierarchical structure enables efficient navigation and retrieval of project data, allowing users to easily find and access specific files or components.
Data Sharing and Collaboration
MicroStation facilitates data sharing and collaboration through its integrated features and tools.
- MicroStation supports various file formats, allowing for seamless data exchange with other CAD applications and external software.
- The software provides tools for version control, ensuring that multiple users can work on the same project without overwriting each other’s changes.
- MicroStation allows for the creation of shared design environments, where multiple users can collaborate on a project simultaneously, viewing and editing data in real-time.
- The ability to share project data across different platforms and devices enhances communication and collaboration among team members, regardless of their physical location.
MicroStation Customization
MicroStation is a powerful and flexible CAD software that offers a wide range of customization options to meet the specific needs of users. This flexibility allows users to tailor the software to their workflows, enhance productivity, and streamline their design processes.
Customization Options
Customization options in MicroStation allow users to modify the software’s interface, functionality, and workflows to suit their preferences and specific requirements. These options include:
- Workspaces: Users can create custom workspaces that organize tools, menus, and panels in a way that optimizes their workflow. Workspaces can be tailored to specific tasks, projects, or user preferences.
- Keyboards and Mouse: Users can configure keyboard shortcuts and mouse actions to execute commands and access tools quickly and efficiently. This can significantly improve productivity by reducing the need for repetitive mouse clicks or menu navigation.
- Toolbars and Menus: MicroStation allows users to customize toolbars and menus by adding, removing, or rearranging tools and commands. This enables users to create a personalized interface that prioritizes frequently used tools and simplifies access to essential commands.
- Settings and Preferences: Users can adjust various settings and preferences to control the behavior of MicroStation. This includes options for drawing units, display settings, file handling, and other aspects of the software’s operation.
Macros and Scripts
Macros and scripts play a crucial role in customizing MicroStation functionality. They allow users to automate repetitive tasks, create custom tools, and extend the software’s capabilities.
- Macros: Macros are sequences of commands that can be recorded and executed with a single click. They automate repetitive tasks such as drawing lines, creating circles, or applying specific design settings. For example, a macro could be created to automatically generate a standard title block with company information and project details.
- Scripts: Scripts are more advanced than macros and offer greater flexibility and control. They are written in a programming language, such as VBA or Python, and can perform complex tasks such as manipulating data, creating custom dialog boxes, or interacting with external applications. Scripts can be used to create custom tools that streamline workflows and enhance design processes. For example, a script could be written to automate the creation of a complex 3D model based on user-defined parameters.
“Macros and scripts are powerful tools for extending the functionality of MicroStation and customizing it to meet specific user needs.”
Example of Customization
A civil engineer working on a highway design project could customize MicroStation to streamline their workflow by:
- Creating a custom workspace with tools and panels specific to highway design, such as tools for creating road alignments, cross sections, and drainage structures.
- Configuring keyboard shortcuts to access frequently used commands quickly.
- Creating a macro to automatically generate a standard title block for highway design drawings.
- Developing a script to automate the creation of cross sections based on predefined parameters.
These customizations would significantly improve the engineer’s efficiency and accuracy by reducing repetitive tasks, simplifying access to essential tools, and automating complex calculations.
MicroStation Training and Resources
MicroStation offers various training programs and resources to help users learn and master the software. These programs cater to different skill levels, from beginners to advanced users, and cover a wide range of topics, including basic functionalities, advanced modeling techniques, and industry-specific applications.
Training Programs
MicroStation training programs are available in various formats, including online courses, instructor-led classes, and self-paced tutorials. These programs provide a structured learning experience, covering theoretical concepts and practical exercises.
- Bentley Institute: Bentley Institute offers a comprehensive range of MicroStation training programs, covering various aspects of the software. These programs are delivered through online courses, instructor-led classes, and self-paced tutorials.
- Authorized Training Partners: Bentley Institute has a network of authorized training partners worldwide, offering MicroStation training programs tailored to specific industries and regions.
- Online Learning Platforms: Several online learning platforms, such as Udemy and Coursera, offer MicroStation training courses. These courses are often more affordable than traditional classroom training programs.
Learning Resources
Besides formal training programs, various resources are available to help users learn and use MicroStation effectively. These resources include online documentation, tutorials, forums, and communities.
- Bentley Documentation: Bentley provides comprehensive documentation for MicroStation, covering all aspects of the software, from basic functionalities to advanced features. This documentation is available online and in PDF format.
- Online Tutorials: Numerous online tutorials are available on platforms like YouTube and websites dedicated to CAD software. These tutorials cover various topics, from basic commands to advanced modeling techniques.
- Online Communities: Online communities, such as Bentley Communities and CAD forums, provide a platform for users to connect, share knowledge, and seek assistance. These communities are valuable resources for learning and troubleshooting.
Learning Materials
| Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Tutorials | Step-by-step guides that teach specific skills and techniques. | “MicroStation for Beginners: A Complete Guide” |
| Documentation | Comprehensive manuals and guides that provide detailed information about the software’s features and functionalities. | “MicroStation User Guide” |
| Online Communities | Platforms where users can connect, share knowledge, and seek assistance. | Bentley Communities, CAD Forums |
MicroStation Industry Trends
The CAD software industry is continuously evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing user needs. MicroStation, as a leading CAD software, is adapting to these trends and integrating new technologies to enhance its capabilities and user experience.
Impact of Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies are significantly influencing the CAD software landscape, impacting MicroStation’s development and future direction. These technologies are driving innovation and creating new opportunities for MicroStation users.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being incorporated into CAD software to automate tasks, improve design efficiency, and enhance user experience. MicroStation is exploring the use of AI for tasks such as design optimization, clash detection, and intelligent data analysis. For example, AI algorithms can analyze design data to identify potential problems or suggest design improvements, leading to more efficient and effective workflows.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud computing enables users to access and collaborate on projects remotely, improving accessibility and flexibility. MicroStation is embracing cloud technologies, offering cloud-based solutions for data storage, collaboration, and rendering. This allows users to access MicroStation and their projects from anywhere with an internet connection, fostering a more collaborative and mobile work environment.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR): VR/AR technologies are revolutionizing visualization and interaction with designs. MicroStation is integrating VR/AR capabilities to enable users to experience their designs in immersive 3D environments. This allows for better visualization, communication, and collaboration, enhancing the design process and enabling more informed decision-making.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The IoT connects physical objects to the internet, enabling data collection and real-time monitoring. MicroStation is integrating IoT capabilities to enable users to incorporate real-time data into their designs. This allows for data-driven design decisions and optimized performance, improving the efficiency and effectiveness of infrastructure projects.
Future Directions and Potential Developments
MicroStation is constantly evolving to meet the changing needs of its users and stay ahead of industry trends. The software is expected to incorporate new features and functionalities driven by emerging technologies.
- Enhanced User Interface: MicroStation is likely to see improvements in its user interface, aiming for a more intuitive and user-friendly experience. This could involve simplifying workflows, providing more context-sensitive tools, and enhancing the overall user experience.
- Integration with Other Software: MicroStation is expected to enhance its integration with other software applications, such as BIM software and data management systems. This will enable seamless data exchange and collaboration across different platforms, fostering a more connected and efficient workflow.
- Advanced Visualization and Analysis Tools: MicroStation is likely to develop more advanced visualization and analysis tools, enabling users to gain deeper insights from their design data. This could involve incorporating AI-powered analytics, advanced visualization techniques, and data-driven design tools.
- Sustainable Design Features: As sustainability becomes increasingly important in design, MicroStation is likely to incorporate features that support sustainable design practices. This could involve tools for analyzing environmental impact, optimizing energy efficiency, and promoting sustainable material choices.
Final Summary
In conclusion, MicroStation stands as a testament to the power of CAD software in revolutionizing the design process. Its comprehensive features, industry-specific applications, and seamless integration capabilities have made it an indispensable tool for engineers, architects, and designers worldwide. As technology continues to advance, MicroStation is poised to remain at the forefront of CAD innovation, enabling professionals to push the boundaries of design and create remarkable projects that shape our world.
Microstation is a powerful software for creating and managing large-scale engineering designs, often used for infrastructure projects. While Microstation excels in these areas, for architectural and building information modeling (BIM) tasks, many professionals prefer to use revit software. Revit’s focus on building design and its integration with other BIM tools makes it a popular choice for projects requiring detailed building models and comprehensive project management.
