Music production software has revolutionized the way music is created, giving anyone with a computer the power to craft their own sonic masterpieces. From the humble beginnings of simple MIDI sequencers to the sophisticated digital audio workstations (DAWs) of today, music production software has evolved dramatically, offering a wide range of tools and features for composing, recording, editing, mixing, and mastering music.
Table of Contents
The software landscape is diverse, with options catering to different budgets, experience levels, and musical genres. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or a budding musician, there’s a music production software out there that can help you bring your musical visions to life.
Introduction to Music Production Software

Music production software has revolutionized the way music is created, providing musicians, producers, and sound engineers with powerful tools to compose, arrange, record, edit, and mix their music. These software applications have become indispensable for creating professional-quality music, offering a wide range of features and functionalities that cater to diverse needs and workflows.
Evolution of Music Production Software
Music production software has evolved significantly since its inception, undergoing a series of transformative milestones and advancements.
- Early Days (1980s-1990s): The first generation of music production software emerged in the 1980s, with programs like C-Lab Notator and Steinberg Cubase paving the way for digital audio workstations (DAWs). These early DAWs offered basic features for recording, editing, and sequencing audio, laying the foundation for modern music production software.
- Rise of Digital Audio (1990s-2000s): The 1990s witnessed a surge in digital audio technology, leading to advancements in sound quality, processing power, and user interfaces. DAWs like Pro Tools and Logic Pro became industry standards, offering comprehensive features for recording, editing, mixing, and mastering music. This period also saw the introduction of virtual instruments, plugins, and other tools that expanded the creative possibilities for music producers.
- Modern Era (2000s-Present): The 21st century has brought about a new era of music production software, characterized by user-friendly interfaces, advanced features, and affordability. DAWs like Ableton Live, FL Studio, and GarageBand have gained popularity for their intuitive workflows and creative tools, making music production accessible to a wider audience. This period has also witnessed the rise of cloud-based DAWs, providing greater flexibility and collaboration opportunities.
Core Functionalities and Features
Music production software typically shares a set of core functionalities and features, designed to facilitate the music creation process.
- Audio Recording: This feature allows users to capture audio signals from microphones, instruments, or other audio sources, enabling the recording of vocals, instruments, and other sounds.
- Audio Editing: DAWs provide a wide range of tools for editing recorded audio, including trimming, cutting, pasting, and applying effects. These features allow users to refine their recordings, remove unwanted noise, and shape the overall sound.
- MIDI Sequencing: MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface) is a protocol that allows communication between musical instruments and computers. DAWs offer MIDI sequencing features that enable users to create and edit musical sequences using virtual instruments, drum machines, and other MIDI-compatible devices.
- Virtual Instruments: Music production software often includes a library of virtual instruments, which emulate the sound of real instruments such as pianos, guitars, drums, and synthesizers. These instruments offer a wide range of sounds and creative possibilities, allowing users to create music without the need for physical instruments.
- Effects Processing: DAWs provide a variety of audio effects, including reverb, delay, equalization, compression, and distortion. These effects can be used to enhance the sound of audio tracks, create unique sonic textures, and shape the overall mix.
- Mixing and Mastering: DAWs offer tools for mixing and mastering audio tracks, allowing users to balance the levels of different instruments and vocals, adjust the overall tone and dynamics, and prepare their music for distribution.
Types of Music Production Software
Music production software encompasses a wide range of tools that empower musicians, producers, and sound engineers to create, edit, and manipulate audio. Understanding the different types of software available is crucial for selecting the right tools for your specific needs and workflow.
Digital Audio Workstations (DAWs)
DAWs are the central hub of music production, providing a comprehensive environment for recording, editing, mixing, and mastering audio. They offer a wide range of features, including:
- Multi-track recording: DAWs allow you to record multiple audio tracks simultaneously, enabling the creation of complex arrangements.
- MIDI sequencing: DAWs facilitate the creation and editing of MIDI data, which represents musical notes and controller information.
- Virtual instruments: Many DAWs include a library of virtual instruments, such as synthesizers, drum machines, and samplers.
- Audio effects: DAWs offer a vast array of audio effects, including reverb, delay, equalization, and compression, to enhance and shape sound.
- Mixing and mastering tools: DAWs provide tools for mixing and mastering audio, including automation, panning, and dynamic processing.
Popular DAWs include:
- Ableton Live: Known for its intuitive workflow and live performance capabilities, Ableton Live is a favorite among electronic music producers.
- Logic Pro X: Developed by Apple, Logic Pro X is a powerful and comprehensive DAW, particularly popular among Mac users.
- FL Studio: A popular choice for hip-hop and electronic music producers, FL Studio is known for its step sequencer and extensive plugin library.
- Pro Tools: Industry-standard DAW widely used in professional studios, Pro Tools offers advanced features and a robust plugin ecosystem.
- Studio One: Studio One is a user-friendly DAW that focuses on ease of use and workflow efficiency.
MIDI Sequencers
MIDI sequencers specialize in creating and editing MIDI data. They are essential for composing and arranging music using virtual instruments and synthesizers.
- Ableton Live: Ableton Live, in addition to its DAW capabilities, excels as a MIDI sequencer, offering powerful features for creating and manipulating MIDI data.
- Logic Pro X: Logic Pro X provides a comprehensive MIDI sequencer with advanced editing tools and automation features.
- FL Studio: FL Studio’s step sequencer is particularly well-suited for creating and editing drum patterns and other rhythmic sequences.
- Cubase: Cubase is a powerful DAW with advanced MIDI sequencing capabilities, including score editing and notation tools.
- Reason: Reason is a unique software package that combines a DAW with a virtual rack of instruments and effects. Its sequencer is highly regarded for its intuitive workflow and creative features.
Virtual Instruments
Virtual instruments are software-based emulations of real-world musical instruments, providing a wide range of sounds and sonic possibilities.
- Native Instruments Komplete: Komplete is a comprehensive suite of virtual instruments, including synthesizers, samplers, and orchestral libraries.
- Arturia V Collection: V Collection offers a range of emulations of classic analog synthesizers, including the Minimoog, ARP 2600, and Juno-106.
- Spectrasonics Omnisphere: Omnisphere is a powerful and versatile synthesizer with a vast library of sounds and advanced sound design features.
- Kontakt: Kontakt is a powerful sampler that allows you to load and play back custom samples, as well as use a wide range of built-in instruments.
- EastWest Symphonic Orchestra: Symphonic Orchestra provides a realistic and detailed orchestral library with a wide range of instruments and articulations.
Audio Editors
Audio editors are specialized software designed for editing and manipulating audio recordings. They offer tools for:
- Trimming and cutting: Audio editors allow you to precisely trim and cut audio recordings.
- Fading and crossfading: They provide tools for creating fades and crossfades between audio clips.
- Noise reduction and restoration: Audio editors offer features for reducing noise and restoring damaged audio.
- Time stretching and pitch shifting: They allow you to adjust the tempo and pitch of audio recordings.
- Audio effects: Many audio editors include a selection of audio effects for enhancing and shaping sound.
Popular audio editors include:
- Audacity: Audacity is a free and open-source audio editor, popular for its simplicity and versatility.
- Adobe Audition: Audition is a powerful audio editor with advanced features for professional audio production.
- Izotope RX: RX is a specialized audio editor focused on noise reduction, restoration, and audio repair.
- Waveform: Waveform is a comprehensive audio editor from Tracktion Software, offering a wide range of features and a user-friendly interface.
- Sound Forge: Sound Forge is a professional audio editor from MAGIX, known for its advanced features and powerful tools.
| Software | Category | Features | Pricing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ableton Live | DAW, MIDI Sequencer | Multi-track recording, MIDI sequencing, virtual instruments, audio effects, live performance features | $129 (Standard), $299 (Suite) |
| Logic Pro X | DAW, MIDI Sequencer | Multi-track recording, MIDI sequencing, virtual instruments, audio effects, extensive plugin library | $199 |
| FL Studio | DAW, MIDI Sequencer | Multi-track recording, step sequencer, virtual instruments, audio effects, lifetime updates | $208 (Producer Edition), $349 (Signature Bundle) |
| Pro Tools | DAW | Industry-standard DAW, advanced features, robust plugin ecosystem | $34.99 (Monthly), $299 (Perpetual) |
| Studio One | DAW | User-friendly interface, workflow efficiency, drag-and-drop functionality | $149 (Artist), $399 (Professional) |
| Native Instruments Komplete | Virtual Instruments | Comprehensive suite of virtual instruments, including synthesizers, samplers, and orchestral libraries | $599 (Komplete 14 Select), $1,199 (Komplete 14 Ultimate) |
| Arturia V Collection | Virtual Instruments | Emulations of classic analog synthesizers, including the Minimoog, ARP 2600, and Juno-106 | $499 (V Collection 9) |
| Spectrasonics Omnisphere | Virtual Instrument | Powerful and versatile synthesizer with a vast library of sounds and advanced sound design features | $499 |
| Kontakt | Virtual Instrument | Powerful sampler that allows you to load and play back custom samples, as well as use a wide range of built-in instruments | $199 |
| EastWest Symphonic Orchestra | Virtual Instrument | Realistic and detailed orchestral library with a wide range of instruments and articulations | $299 (Play), $499 (Diamond) |
| Audacity | Audio Editor | Free and open-source audio editor, simple and versatile | Free |
| Adobe Audition | Audio Editor | Powerful audio editor with advanced features for professional audio production | $20.99 (Monthly), $239.88 (Annual) |
| Izotope RX | Audio Editor | Specialized audio editor focused on noise reduction, restoration, and audio repair | $129 (Standard), $349 (Advanced) |
| Waveform | Audio Editor | Comprehensive audio editor from Tracktion Software, offering a wide range of features and a user-friendly interface | $149 (Free Trial Available) |
| Sound Forge | Audio Editor | Professional audio editor from MAGIX, known for its advanced features and powerful tools | $149 (Audio Studio 15), $349 (Sound Forge Pro 15) |
Key Features of Music Production Software
Music production software offers a diverse set of tools that empower musicians, producers, and sound engineers to create, edit, and refine audio and musical compositions. These features are essential for transforming raw ideas into polished audio recordings.
Audio Recording and Editing Capabilities
Audio recording and editing are fundamental aspects of music production. Modern software provides users with advanced tools for capturing audio signals from microphones, instruments, and other sources. These capabilities enable users to:
- Capture High-Quality Audio: Software incorporates high-resolution audio recording at various sample rates and bit depths, ensuring fidelity and clarity in recordings.
- Edit and Manipulate Audio: Features like cutting, trimming, and splicing allow users to edit audio segments with precision.
- Apply Audio Effects: Software includes a wide range of built-in effects, such as reverb, delay, equalization, and compression, allowing users to enhance and shape the sound of their recordings.
- Automate Audio Processing: Automation features allow users to create dynamic changes in volume, effects, and other parameters over time, adding depth and complexity to recordings.
MIDI Sequencing and Virtual Instruments
MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface) is a protocol that allows electronic musical instruments and computers to communicate. MIDI sequencing involves arranging and programming musical notes, rhythms, and other musical data using software. This process enables users to:
- Compose and Arrange Music: MIDI sequencers provide a user-friendly interface for entering notes, creating melodies, and arranging musical ideas.
- Use Virtual Instruments: Software often includes a library of virtual instruments, which are software simulations of real-world instruments like pianos, drums, guitars, and synthesizers. This allows users to experiment with a wide range of sounds without needing physical instruments.
- Control External Instruments: MIDI sequencers can control external hardware instruments, allowing users to integrate physical instruments into their productions.
Mixing and Mastering Tools
Mixing and mastering are crucial stages in the music production process. Mixing involves balancing and adjusting the levels of individual audio tracks to create a cohesive and balanced sound. Mastering involves optimizing the overall sound quality of a track for distribution. Music production software offers features that facilitate these processes:
- Mixing Console: Software includes virtual mixing consoles with multiple channels, allowing users to control the levels, panning, and effects of individual audio tracks.
- EQ (Equalization): EQ tools allow users to adjust the frequency content of audio tracks, shaping the tonal balance and removing unwanted frequencies.
- Compression: Compression tools help to control the dynamic range of audio, ensuring that quiet sounds are audible without loud sounds becoming distorted.
- Reverb and Delay: These effects create the illusion of space and depth, adding realism and dimension to audio recordings.
- Mastering Tools: Software includes tools for mastering, such as limiters, equalizers, and stereo imagers, which help to optimize the loudness, clarity, and overall sonic quality of a track for distribution.
Choosing the Right Music Production Software
Choosing the right music production software is a crucial step in your musical journey. It’s like selecting the right tools for a craftsman – the right software can empower you to create amazing music, while the wrong one can hinder your progress and frustrate your creative flow.
Factors to Consider
When choosing music production software, several factors play a significant role in determining the best fit for your needs. These factors can be broadly categorized into budget, experience level, musical genre, and desired features.
- Budget: Music production software comes in a wide range of prices, from free options to professional-grade suites that cost hundreds of dollars. Consider your budget and prioritize the features that are most important to you. Free options can be great for beginners, while paid software often offers more advanced features and support.
- Experience Level: If you’re a beginner, a user-friendly interface and a good selection of tutorials can make a big difference. Experienced producers may prefer software with advanced features and flexibility. Look for software that caters to your current skill level and offers a learning curve that suits your pace.
- Musical Genre: Different genres of music often require different tools. For example, electronic music producers may need software with powerful synthesis and sound design features, while hip-hop producers might prioritize drum sampling and beat-making tools. Consider the genre you want to produce and choose software that provides the right tools for the job.
- Desired Features: Music production software offers a wide array of features, including virtual instruments, audio effects, MIDI editors, mixing consoles, and mastering tools. Identify the features that are essential for your workflow and choose software that meets your needs.
Evaluating Software Options
Once you’ve considered the key factors, it’s time to evaluate different software options. Here are some tips and strategies to help you make an informed decision:
- User Reviews: Read user reviews from other producers to get insights into the software’s strengths and weaknesses. Look for reviews from users with similar experience levels and musical genres to your own. Websites like Reddit, Gearslutz, and KVR Audio are excellent resources for user reviews.
- Tutorials and Demos: Many software developers offer free tutorials and demos to help you learn the basics and explore the features. Try out different software options and see which one feels most intuitive and comfortable to use.
- Free Trials: Take advantage of free trials to test out software before making a purchase. This gives you a chance to experience the software firsthand and see if it meets your needs.
Guide for Beginners
Choosing your first music production software can be overwhelming, but here’s a simple guide to help you get started:
- Start with Free Options: Free software like GarageBand (Mac), Audacity, or LMMS are excellent starting points. They provide a solid foundation in music production and can help you learn the basics without any upfront cost.
- Focus on User-Friendliness: Look for software with a clear and intuitive interface. Tutorials and online communities can also provide valuable support for beginners.
- Don’t Be Afraid to Experiment: Try out different software options and find one that you enjoy using. The most important thing is to have fun and explore your creativity.
Essential Tools and Techniques
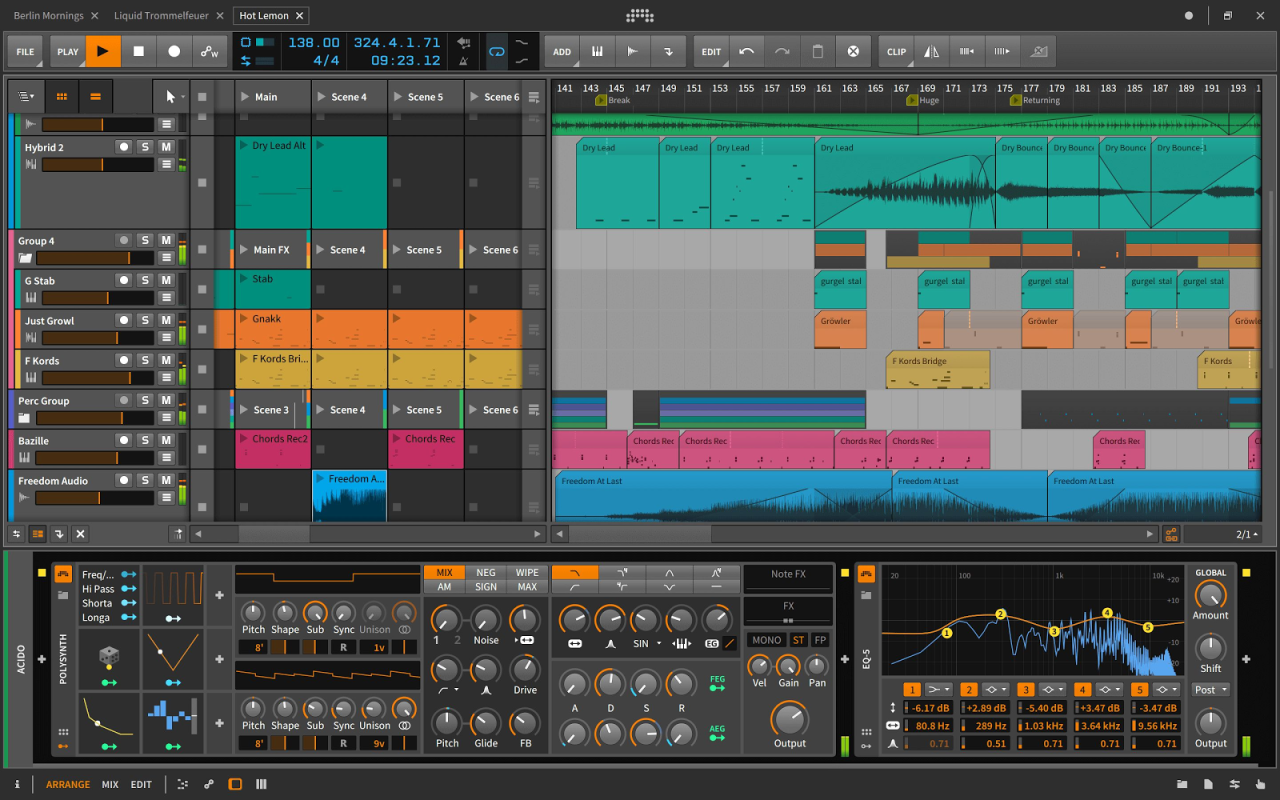
Music production software offers a vast array of tools and techniques to shape and enhance your audio, transforming raw recordings into polished tracks. This section delves into essential tools and techniques that empower you to elevate your productions.
Audio Plugins
Audio plugins are digital tools that add effects, processing, and functionality to your audio. They can enhance sound quality, create unique effects, and shape the overall character of your tracks.
Plugins can be categorized into various types, including:
– Effects plugins: Alter the timbre, dynamics, or spatial characteristics of audio, such as reverb, delay, chorus, and distortion.
– Instrument plugins: Simulate real-world instruments or create entirely new sounds, like synthesizers, samplers, and drum machines.
– Utility plugins: Provide essential tools for audio processing, such as equalizers, compressors, and limiters.
Plugins are available in various formats, including VST, AU, and AAX. These formats allow plugins to be used across different DAWs.
- Equalizers: Used to adjust the frequency content of audio. This can be used to boost or cut specific frequencies, shape the tonal balance of instruments, or remove unwanted noise.
- Compressors: Used to reduce the dynamic range of audio, making quieter sounds louder and louder sounds softer. This can be used to even out the volume of a track or create a more consistent dynamic range.
- Reverb: Simulates the sound of a room or space, adding depth and realism to audio. This can be used to create a sense of space, add ambience, or enhance the clarity of instruments.
- Delay: Creates echoes or repetitions of audio, adding texture and movement to a track. This can be used to create rhythmic patterns, add space, or create a sense of depth.
Recording, Editing, Mixing, and Mastering
The music production process typically involves several stages: recording, editing, mixing, and mastering.
Recording
The recording process captures audio signals from instruments, vocals, or other sources. This involves setting up microphones, connecting instruments, and recording the audio into the DAW.
- Setting up the recording environment: This includes choosing a quiet space with minimal noise, setting up microphones, and connecting instruments to the audio interface.
- Recording audio: Once the recording environment is set up, you can start recording audio. This involves selecting the appropriate recording settings, monitoring the audio levels, and capturing the desired performance.
- Monitoring audio levels: It’s essential to monitor audio levels during recording to prevent clipping (distortion caused by overloading the audio signal).
Editing
Editing involves refining the recorded audio, removing unwanted noise, and adjusting the timing and pitch of audio.
- Trimming and cutting: This involves removing unwanted sections of audio, such as silence or mistakes.
- Quantizing: This process aligns audio to a specific beat or grid, ensuring that the timing is accurate and consistent.
- Pitch correction: Used to adjust the pitch of audio, correcting mistakes or creating vocal harmonies.
Mixing
Mixing combines all the recorded audio tracks into a cohesive and balanced mix. This involves adjusting the volume, panning, and equalization of each track to create a balanced and engaging sound.
- Volume balancing: Adjusting the volume of each track to create a balanced mix, ensuring that all instruments and vocals are heard clearly.
- Panning: Placing instruments and vocals in the stereo field, creating a sense of width and depth.
- Equalization: Adjusting the frequency content of each track, shaping the tonal balance and removing unwanted frequencies.
- Adding effects: Applying effects, such as reverb, delay, and chorus, to enhance the sound of individual tracks or the overall mix.
Mastering
Mastering is the final stage of the production process, where the mix is polished and prepared for distribution. This involves adjusting the overall volume, dynamics, and stereo image of the track to ensure that it sounds loud, clear, and professional.
- Volume maximization: Increasing the overall volume of the track without introducing distortion or clipping.
- EQ and dynamics processing: Making final adjustments to the frequency content and dynamic range of the track.
- Stereo imaging: Adjusting the stereo width and depth of the track to create a balanced and engaging listening experience.
Organizing Projects and Managing Audio Files
Organizing your projects and managing your audio files is crucial for efficient workflow and easy access to your work.
- Create a consistent file naming system: This helps you easily identify and locate your audio files.
- Organize your projects into folders: This allows you to keep related files together and easily find the projects you need.
- Use a tagging system: Tagging your audio files with relevant s allows you to quickly search and filter your library.
- Backup your work regularly: This ensures that you don’t lose any valuable data.
The Future of Music Production Software
The world of music production is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and the changing needs of artists. As we move forward, music production software is poised to become even more powerful, intuitive, and accessible, pushing the boundaries of creative expression.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Music Production, Music production software
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are revolutionizing the music production landscape, offering new possibilities for composition, arrangement, and sound design.
AI-powered tools are being used to:
- Generate melodies and harmonies: AI algorithms can analyze existing music and generate new musical ideas based on specific styles and preferences.
- Compose entire tracks: Some AI tools can create complete songs, including arrangements, instrumentation, and even vocals.
- Enhance existing recordings: AI can be used to improve the quality of audio recordings, removing noise, enhancing clarity, and even adding effects.
- Create personalized music experiences: AI can learn from your listening habits and preferences to create personalized playlists and recommendations.
The impact of AI and ML on music production is significant. It allows producers to explore new creative avenues, automate repetitive tasks, and achieve results that were previously impossible. While some may worry that AI will replace human creativity, it is more likely to become a powerful tool that empowers producers and expands their artistic possibilities.
Resources and Learning Materials
Learning music production software can be a rewarding journey, and there are numerous resources available to help you along the way. This section will provide you with a curated list of online resources, tutorials, forums, communities, books, and courses that can guide you in mastering the art of music production.
Online Resources
The internet is a treasure trove of information and learning materials for music production. Here are some websites and platforms that offer valuable resources for aspiring producers:
- YouTube: YouTube is a fantastic platform for finding tutorials, tips, and tricks from experienced producers. Search for specific software tutorials, techniques, or genres to find relevant content. Many creators offer free and paid courses on YouTube, allowing you to learn at your own pace.
- SoundCloud: SoundCloud is a popular platform for sharing and discovering music. It’s a great place to find inspiration, connect with other producers, and learn from their work. Many producers upload their projects, tutorials, and behind-the-scenes content, offering insights into their creative process.
- Reddit: Reddit is a vibrant online community with several subreddits dedicated to music production. These subreddits provide a platform for discussion, questions, and sharing knowledge. You can find valuable advice, tips, and resources from experienced producers.
- Producer Forums: Online forums dedicated to music production are great for finding answers to specific questions, engaging in discussions, and connecting with other producers. Some popular forums include Gearslutz, KVR Audio, and MusicRadar.
Tutorials and Courses
Tutorials and courses provide structured learning paths for mastering music production software.
- Udemy: Udemy offers a wide range of online courses on music production, covering various software and techniques. Many courses are taught by experienced producers and industry professionals, offering comprehensive training and practical skills.
- Skillshare: Skillshare is another platform offering online courses on music production, covering topics like mixing, mastering, and songwriting. They often feature courses taught by industry professionals, providing valuable insights and practical techniques.
- Coursera: Coursera offers online courses from renowned universities and institutions, including music production courses. These courses often provide a more academic approach to music production, covering theoretical concepts and practical applications.
- Online Music Production Schools: Several online music production schools offer comprehensive programs that cover various aspects of music production. These programs often include personalized feedback from instructors, providing a structured learning experience.
Books and Resources
Books can provide a deeper understanding of music production concepts and techniques.
- “The Complete Guide to Music Production” by Michael New: This comprehensive book covers various aspects of music production, from basic concepts to advanced techniques. It’s a valuable resource for aspiring producers of all levels.
- “Mixing Secrets for the Small Studio” by Mike Senior: This book focuses on the art of mixing, providing practical tips and techniques for achieving professional-sounding mixes. It’s a must-read for producers who want to improve their mixing skills.
- “The Sound Design Bible” by Richard Devine: This book delves into the world of sound design, exploring various techniques and tools for creating unique and interesting sounds. It’s a valuable resource for producers who want to expand their sonic palette.
- “Music Theory for Computer Musicians” by Michael New: This book covers music theory concepts relevant to music production, providing a solid foundation for understanding musical structure and composition.
Case Studies and Examples
Music production software has played a pivotal role in shaping modern music, empowering producers and artists to create groundbreaking sounds and push the boundaries of musical expression. Examining the techniques and workflows employed by successful producers can provide valuable insights into the impact of these tools on the evolution of music genres.
Successful Producers and Their Software Choices
The choice of music production software often reflects a producer’s individual workflow and artistic vision.
- Skrillex – A pioneer of dubstep and electronic dance music, Skrillex has heavily relied on Ableton Live for its intuitive workflow and real-time performance capabilities. His signature sound, characterized by intricate sound design and layered textures, is facilitated by Ableton’s powerful features like sample manipulation and effects processing.
- Kanye West – Known for his innovative and genre-bending productions, Kanye West primarily utilizes Pro Tools, a software renowned for its robust audio editing and mixing capabilities. His intricate production techniques, incorporating diverse instruments and samples, benefit from Pro Tools’ comprehensive toolset and vast plugin library.
- The Chainsmokers – This electronic music duo has achieved mainstream success using Logic Pro X, a software known for its user-friendly interface and wide range of virtual instruments. Their signature sound, often featuring catchy melodies and intricate synth arrangements, is facilitated by Logic Pro X’s powerful features like MIDI sequencing and its extensive sound library.
Impact of Music Production Software on Genre Evolution
Music production software has been instrumental in the evolution of various music genres, enabling producers to experiment with new sounds and push the boundaries of sonic exploration.
- Hip-hop: The advent of digital audio workstations (DAWs) like Fruity Loops (now FL Studio) revolutionized hip-hop production. The software’s intuitive beat-making capabilities and extensive sample library allowed producers to create complex and intricate beats, contributing to the genre’s evolution from its early roots to its modern-day diversity.
- Electronic Dance Music (EDM): The development of software like Ableton Live and Serato Studio has played a significant role in the rise of EDM. These programs’ real-time performance features and intuitive loop-based workflows have enabled producers to create dynamic and interactive live sets, pushing the boundaries of electronic music performance.
- Pop: Music production software has also had a profound impact on pop music. The use of virtual instruments, advanced audio effects, and sophisticated mixing techniques has allowed producers to create polished and commercially successful pop tracks. Software like Logic Pro X and Pro Tools have become essential tools in the pop production process, enabling producers to create intricate arrangements and layered soundscapes.
Conclusion
Music production software has revolutionized the way music is created, empowering musicians, producers, and sound designers with unprecedented tools and flexibility. From composing melodies and arranging tracks to mixing and mastering, these software programs offer a comprehensive suite of features that cater to diverse musical styles and workflows.
Importance of Music Production Software in Modern Music Creation
The significance of music production software in modern music creation cannot be overstated. These programs have democratized music production, allowing individuals with limited resources and technical expertise to create high-quality music.
- Accessibility: Music production software is readily available, making it accessible to a wider audience.
- Versatility: These programs offer a vast array of tools and instruments, allowing musicians to experiment with different sounds and genres.
- Efficiency: Music production software streamlines the creative process, enabling musicians to work more efficiently and effectively.
End of Discussion
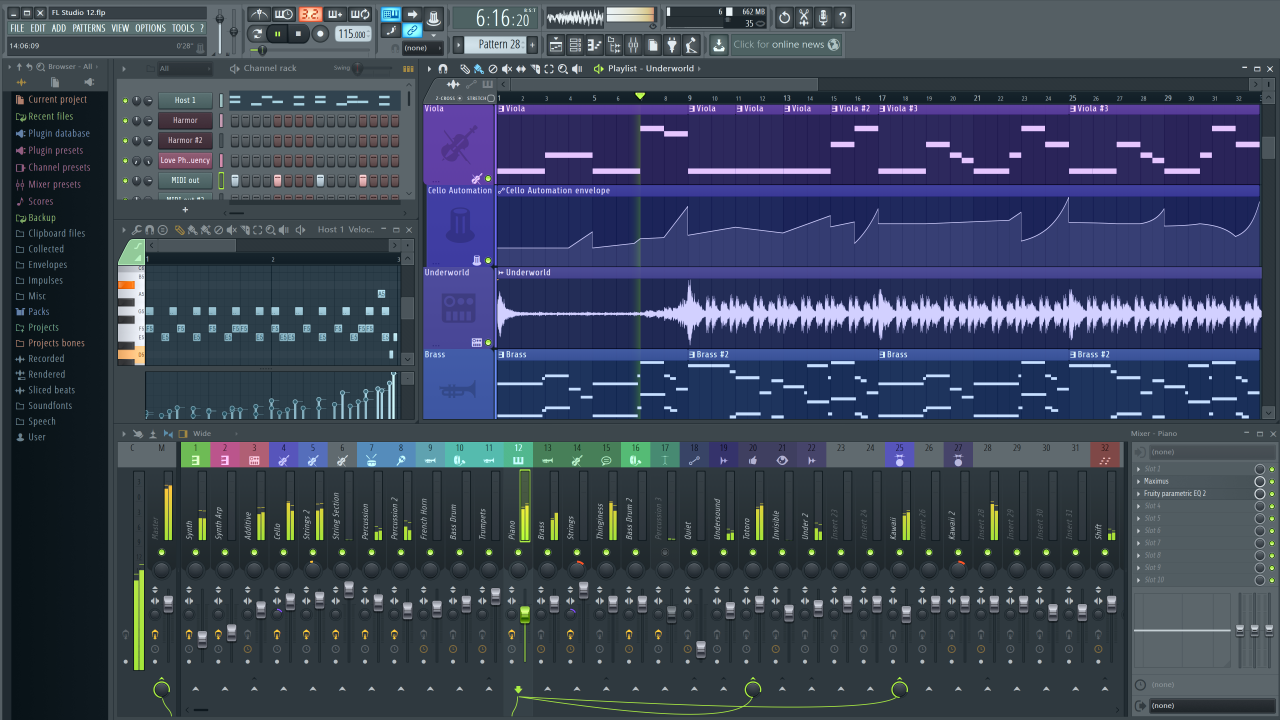
Music production software has democratized music creation, empowering individuals to express their creativity and share their music with the world. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative tools and techniques to emerge, further blurring the lines between the real and the virtual in the realm of music production. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting out, exploring the world of music production software is an exciting journey that can lead to countless creative possibilities.
Music production software has come a long way, offering a wide range of tools for creating and manipulating sound. From digital audio workstations (DAWs) to virtual instruments, the possibilities are endless. One platform that stands out for its user-friendly interface and powerful features is waveapps , a cloud-based solution that allows you to collaborate with others on your projects in real-time.
Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting out, waveapps can help you take your music production to the next level.
