Parallel Desktop is a powerful virtualization software that allows you to run multiple operating systems simultaneously on a single computer. It acts as a bridge, enabling you to seamlessly switch between different operating systems, accessing their unique applications and features without the need for rebooting.
Table of Contents
With Parallel Desktop, you can experience the flexibility of running Windows, Linux, or macOS side-by-side on your Mac. Imagine having your favorite Windows games or professional software readily available alongside your Mac applications, all within the same environment. This versatility opens up a world of possibilities for developers, designers, gamers, and anyone seeking to maximize their computing experience.
Introduction to Parallel Desktop
Parallel Desktop is a virtualization software application that allows you to run operating systems other than your computer’s native operating system on your Mac. It creates a virtual machine (VM) environment, enabling you to install and use Windows, Linux, or other operating systems alongside macOS without needing to reboot your Mac.
Parallel Desktop’s primary purpose is to provide a seamless and convenient way to run multiple operating systems simultaneously on a single Mac. It offers various features, including:
History and Evolution of Parallel Desktop
Parallel Desktop was first released in 2006 by Parallels, a company specializing in virtualization and cross-platform compatibility solutions. It quickly gained popularity for its user-friendliness and performance. Over the years, Parallel Desktop has undergone significant evolution, incorporating new features, improving performance, and enhancing compatibility with the latest macOS and Windows versions.
Key Features and Benefits
Parallel Desktop is a powerful virtualization software that allows you to run multiple operating systems simultaneously on a single Mac. This comprehensive tool offers a range of features and benefits designed to enhance productivity, flexibility, and security.
Virtual Machine Creation and Management
Parallel Desktop simplifies the process of creating and managing virtual machines. You can easily install and configure different operating systems, such as Windows, Linux, or Chrome OS, within a virtual environment. The software provides intuitive tools for customizing virtual machine settings, including memory allocation, storage space, and network connectivity.
Benefits of Running Multiple Operating Systems
Running multiple operating systems simultaneously offers several advantages. You can access applications that are only available on specific operating systems without having to reboot your Mac. This versatility is particularly beneficial for users who need to work with specialized software or access specific services. Additionally, you can test software or applications in different environments before deploying them to your primary operating system.
Compatibility, Performance, and Security
Parallel Desktop is renowned for its compatibility, performance, and security features. It supports a wide range of operating systems and applications, ensuring seamless integration with your existing Mac environment. The software leverages the power of your Mac’s hardware to deliver optimal performance, allowing you to run demanding applications smoothly. Moreover, Parallel Desktop incorporates robust security features, such as virtual machine isolation, to protect your Mac from potential threats.
Use Cases and Applications
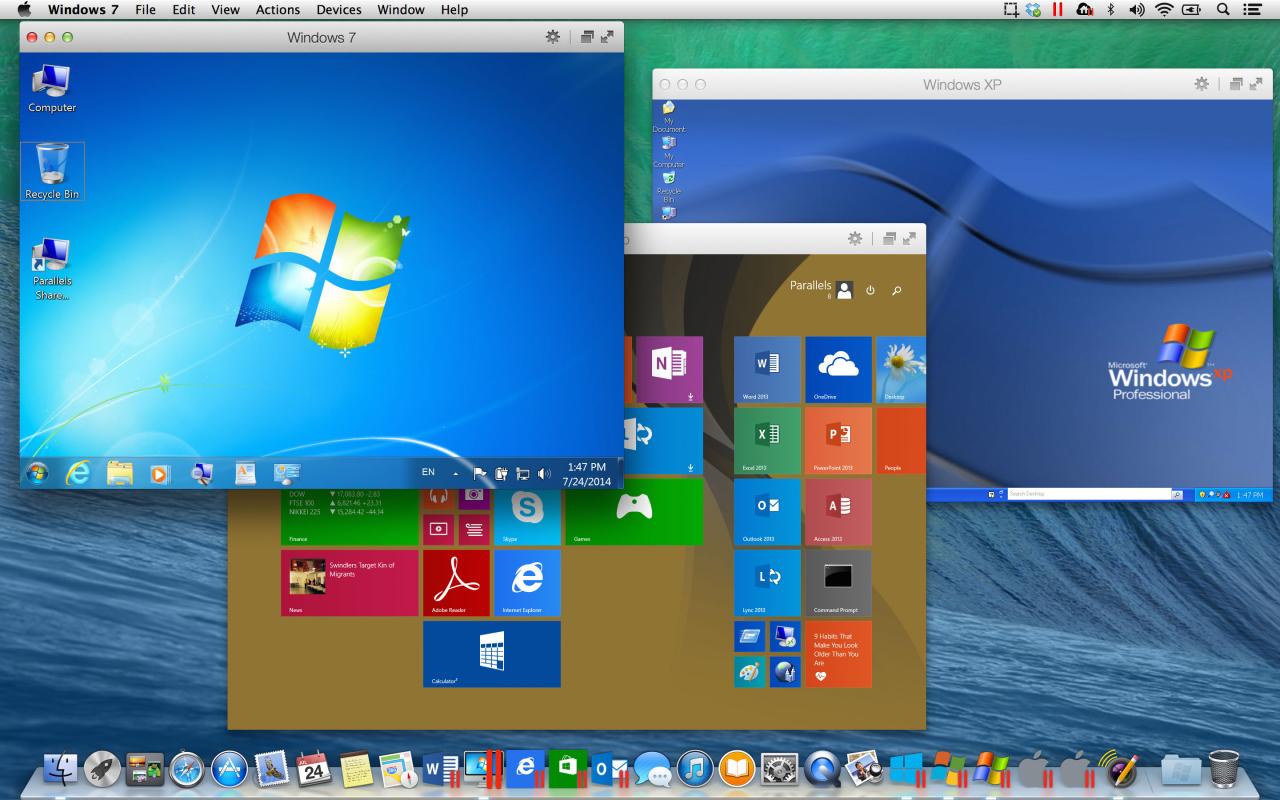
Parallel Desktop offers a versatile platform with a wide range of applications across various industries and professions. Its ability to run multiple operating systems simultaneously empowers users to achieve tasks that would be difficult or impossible with a single operating system.
Software Development and Testing
Software development and testing teams benefit greatly from Parallel Desktop’s ability to create isolated environments for different projects or stages of development. This allows developers to test their applications in various operating systems and configurations without affecting their primary system. For example, a developer can use Parallel Desktop to test a web application in Windows, macOS, and Linux simultaneously, ensuring compatibility across different platforms.
Gaming
Parallel Desktop allows gamers to access a wider range of games by running games designed for other operating systems on their macOS device. This is especially beneficial for gamers who want to play Windows-exclusive games or older games that are not available on macOS.
IT Professionals
IT professionals utilize Parallel Desktop to manage and troubleshoot systems remotely. They can run a virtual machine with the same operating system as the remote computer, allowing them to access and manage files, install software, and troubleshoot issues without physically being present.
Graphic Designers
Graphic designers often need to work with different software applications that are not available on macOS. Parallel Desktop allows them to run Windows-based design software, such as Adobe Photoshop or Illustrator, alongside their macOS applications, providing a seamless workflow.
System Requirements and Compatibility
To ensure smooth operation and optimal performance, Parallel Desktop requires specific system resources and is compatible with a range of operating systems and hardware configurations. This section Artikels the minimum and recommended system requirements, discusses compatibility with different platforms, and provides guidance on achieving optimal performance.
System Requirements, Parallel desktop
Parallel Desktop has minimum and recommended system requirements to guarantee smooth operation and optimal performance. These requirements ensure that your system can handle the demands of running virtual machines efficiently.
- Minimum Requirements:
- Processor: Intel Core 2 Duo or AMD equivalent
- Memory: 4 GB RAM (8 GB recommended)
- Storage: 5 GB free disk space (10 GB recommended)
- Operating System: macOS 10.14 Mojave or later
- Recommended Requirements:
- Processor: Intel Core i5 or AMD equivalent
- Memory: 8 GB RAM (16 GB recommended)
- Storage: 10 GB free disk space (20 GB recommended)
- Operating System: macOS 11 Big Sur or later
Operating System Compatibility
Parallel Desktop is designed to run on macOS and supports a wide range of operating systems within virtual machines.
- Supported Guest Operating Systems:
- Windows: Windows 10, Windows 11, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2022
- Linux: Ubuntu, Fedora, Debian, CentOS, Red Hat Enterprise Linux
- Other: macOS, Chrome OS, Android (with limitations)
Hardware Compatibility
Parallel Desktop leverages the hardware capabilities of your Mac to provide a seamless virtual machine experience. While it generally supports most Macs, some features might require specific hardware components.
- Recommended Hardware:
- Processor: Intel Core i5 or AMD equivalent
- Memory: 8 GB RAM (16 GB recommended)
- Storage: SSD (Solid State Drive) for faster performance
- Graphics: Integrated or dedicated graphics card with at least 2 GB of memory
Ensuring Optimal Performance
To ensure optimal performance and avoid compatibility issues, consider the following tips:
- Allocate Sufficient Resources: Assign adequate CPU cores, RAM, and disk space to your virtual machines.
- Use SSD Storage: SSDs provide significantly faster read and write speeds, leading to improved virtual machine performance.
- Keep Software Updated: Regularly update Parallel Desktop, your Mac’s operating system, and the guest operating systems within your virtual machines.
- Monitor Resource Usage: Regularly monitor CPU usage, RAM consumption, and disk space utilization to identify potential bottlenecks.
Installation and Setup Process: Parallel Desktop
Installing and setting up Parallel Desktop is a straightforward process that involves downloading the software, running the installer, and configuring your virtual machines. The initial setup process includes setting up virtual machines, configuring settings, and troubleshooting common problems.
Downloading and Installing Parallel Desktop
Downloading and installing Parallel Desktop is a simple process. First, you need to purchase a license for Parallel Desktop from the official website. After purchasing the license, you can download the software and run the installer. The installer will guide you through the installation process.
- Visit the Parallels website and download the Parallel Desktop installer.
- Run the installer and follow the on-screen instructions.
- Accept the license agreement and choose the installation location.
- Wait for the installation to complete.
Once the installation is complete, you can launch Parallel Desktop and start creating virtual machines.
Creating and Configuring Virtual Machines
Parallel Desktop allows you to create virtual machines for different operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and macOS. The process of creating a virtual machine involves selecting the operating system, allocating resources, and configuring settings.
- Launch Parallel Desktop and click on the “Create” button.
- Select the operating system you want to install in the virtual machine.
- Choose the virtual machine’s name and location.
- Allocate resources such as RAM, CPU cores, and hard drive space.
- Configure other settings, such as network settings and shared folders.
Once you have configured the virtual machine, you can install the operating system inside it.
Troubleshooting Installation and Setup Problems
Although the installation and setup process is generally straightforward, you may encounter some problems. Common problems include installation errors, virtual machine startup issues, and compatibility issues.
- Installation Errors: If you encounter installation errors, check your system requirements and make sure you have enough disk space. You can also try reinstalling Parallel Desktop or restarting your computer.
- Virtual Machine Startup Issues: If the virtual machine fails to start, check the virtual machine settings and make sure the resources are allocated correctly. You can also try restarting the virtual machine or reinstalling the operating system inside it.
- Compatibility Issues: If you encounter compatibility issues, check the Parallel Desktop documentation for supported operating systems and hardware. You may need to update your drivers or use a different operating system.
Virtual Machine Management
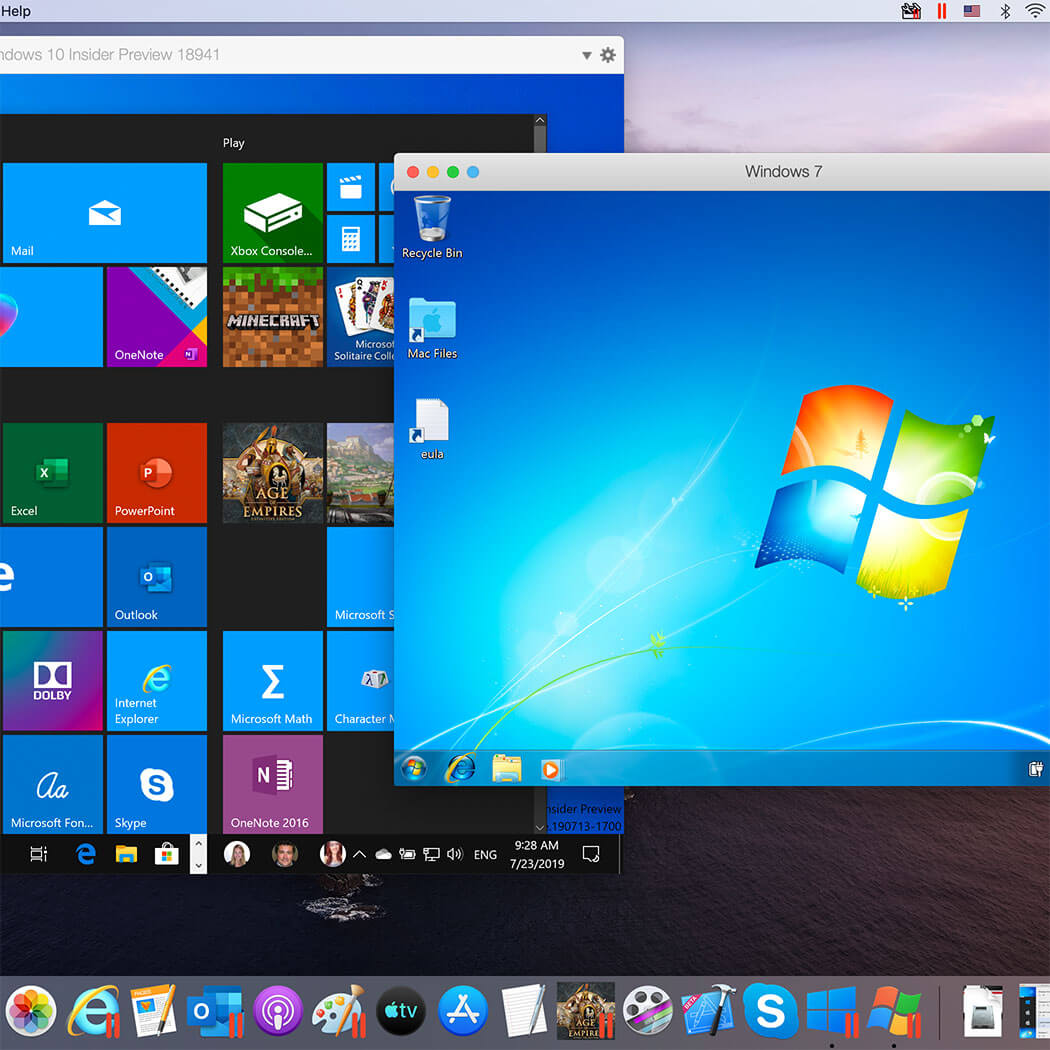
Parallel Desktop empowers you to create, manage, and delete virtual machines with ease, offering a seamless experience for running multiple operating systems on your Mac. Let’s delve into the intricacies of virtual machine management within Parallel Desktop.
Creating Virtual Machines
Creating a virtual machine in Parallel Desktop is a straightforward process. You can either download an operating system image from the internet or use an existing ISO file. Parallel Desktop provides a user-friendly wizard that guides you through the steps.
- Select the Operating System: Choose the operating system you want to install from the list of supported operating systems.
- Name and Location: Provide a name for your virtual machine and specify the location where you want to store its files.
- Resource Allocation: Allocate resources like memory, storage space, and processors to the virtual machine. This ensures optimal performance based on your needs.
- Installation: Parallel Desktop will automatically install the operating system within the virtual machine. You can then configure the operating system just as you would on a physical computer.
Managing Virtual Machines
Once you have created a virtual machine, you can easily manage it from the Parallel Desktop application.
- Start, Stop, and Suspend: Control the virtual machine’s power state with these options.
- Access Virtual Machine Settings: Modify the virtual machine’s settings, including memory allocation, storage space, and network configuration.
- Snapshot and Restore: Create snapshots of your virtual machine’s state to revert to a previous point in time, protecting your work and allowing you to experiment without fear of losing data.
- Sharing Files and Folders: Share files and folders between your Mac and the virtual machine, facilitating seamless collaboration and data exchange.
Customizing Virtual Machine Settings
Parallel Desktop offers extensive customization options to tailor your virtual machine’s performance and behavior to your specific needs.
- Memory Allocation: Adjust the amount of RAM allocated to the virtual machine. More memory allows for smoother performance, especially for demanding applications.
- Storage Space: Allocate the desired amount of hard disk space to the virtual machine. You can choose to create a fixed-size disk or a dynamically expanding disk, depending on your storage requirements.
- Processor Cores: Assign a specific number of processor cores to the virtual machine. This directly impacts the virtual machine’s processing power.
- Network Configuration: Configure the virtual machine’s network settings, including the type of network connection (NAT, Bridged, or Host-Only) and the IP address.
- Display Resolution: Set the display resolution of the virtual machine to match your preference or the requirements of the operating system.
Deleting Virtual Machines
When you no longer need a virtual machine, you can delete it from Parallel Desktop. This removes the virtual machine files and all associated data.
- Select the Virtual Machine: Choose the virtual machine you want to delete from the list of virtual machines in Parallel Desktop.
- Confirm Deletion: Parallel Desktop will prompt you to confirm the deletion. Ensure you have backed up any important data before proceeding.
- Removal: The virtual machine and its files will be permanently deleted from your Mac.
Best Practices for Organizing and Managing Multiple Virtual Machines
Managing multiple virtual machines effectively is crucial for maintaining a streamlined workflow.
- Naming Conventions: Use clear and consistent naming conventions for your virtual machines. This makes it easier to identify and manage them. For example, you could use “Windows 10 – Work” or “Ubuntu 22.04 – Development” to denote the operating system and purpose.
- Organized Storage: Create a dedicated folder on your Mac to store your virtual machine files. This keeps them organized and prevents clutter on your system.
- Regular Backups: Back up your virtual machines regularly to protect your data. Parallel Desktop allows you to create snapshots, which capture the state of your virtual machine at a specific point in time. You can also use external storage devices or cloud storage services to back up your virtual machines.
- Monitor Resource Usage: Keep an eye on the resource usage of your virtual machines. If you are running multiple virtual machines simultaneously, you may need to adjust the resource allocation to ensure optimal performance. You can monitor resource usage in Parallel Desktop’s settings or through the Activity Monitor application on your Mac.
Performance and Optimization
The performance of Parallel Desktop and your virtual machines is influenced by various factors, including the hardware specifications of your host machine, the operating system of your virtual machine, and the applications you run within it. Understanding these factors and implementing optimization techniques can significantly improve your overall experience.
Optimizing Performance
Several strategies can be employed to enhance the performance of Parallel Desktop and your virtual machines.
- Adjusting Settings: Parallel Desktop offers a range of settings that can be customized to optimize performance based on your specific needs. For instance, you can adjust the amount of RAM allocated to the virtual machine, change the processor core allocation, and fine-tune graphics settings. Experimenting with these settings can lead to significant performance gains.
- Managing Resource Allocation: The efficient allocation of resources is crucial for optimal performance. Ensure your host machine has sufficient RAM and processing power to accommodate both your host operating system and the virtual machine. Consider closing unnecessary applications on your host machine to free up resources for your virtual machine. You can also adjust the amount of hard drive space allocated to your virtual machine to ensure sufficient storage for your virtual machine’s operating system and applications.
- Disk Performance: The speed of your hard drive can significantly impact virtual machine performance. Consider using a solid-state drive (SSD) for your host machine, as it offers faster read and write speeds compared to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs). You can also optimize the virtual machine’s hard disk by defragmenting it regularly and ensuring it has enough free space.
Troubleshooting Performance Issues
Performance issues can arise for various reasons, including insufficient resources, software conflicts, or hardware limitations. To identify and resolve these issues, you can follow these steps:
- Check System Resources: Monitor the CPU, RAM, and disk usage of both your host machine and virtual machine to identify any resource bottlenecks. If any of these resources are heavily utilized, it could indicate a performance issue. Consider adjusting resource allocation or closing unnecessary applications to alleviate the bottleneck.
- Review Virtual Machine Settings: Ensure the virtual machine settings are configured appropriately for your needs. Check the RAM allocation, processor core allocation, and graphics settings to ensure they are not limiting performance. You can also try increasing the amount of RAM allocated to the virtual machine to see if it improves performance.
- Update Drivers and Software: Outdated drivers or software can cause performance issues. Ensure your host operating system, virtual machine operating system, and Parallel Desktop software are up to date. You can also check for updates for any applications you run within the virtual machine.
- Check for Conflicts: Software conflicts can also lead to performance issues. Try disabling or uninstalling any recently installed applications on your host machine or virtual machine to see if it resolves the problem.
Security Considerations
Running multiple operating systems in a virtualized environment like Parallel Desktop introduces unique security considerations. It’s essential to understand the potential risks and implement appropriate measures to protect your data and systems.
Security Features of Parallel Desktop
Parallel Desktop incorporates several security features designed to enhance the security of your virtual machines and your host system. These features include:
- Sandboxing: Each virtual machine runs in an isolated environment, preventing malicious software from accessing your host system’s resources. This isolation helps to contain any potential security breaches within the virtual machine.
- Access Control: Parallel Desktop allows you to set specific permissions for each virtual machine, controlling which resources they can access. This granular control helps to limit the impact of any security vulnerabilities within a virtual machine.
Best Practices for Securing Virtual Machines
In addition to the security features provided by Parallel Desktop, you can further enhance the security of your virtual machines by implementing these best practices:
- Keep Operating Systems and Software Updated: Regularly update the operating systems and software running within your virtual machines to patch security vulnerabilities and reduce the risk of attacks.
- Use Strong Passwords: Employ strong passwords for your virtual machine accounts and ensure they are different from the passwords you use for your host system. This prevents unauthorized access to your virtual machines.
- Enable Firewall Protection: Configure the firewall settings on your virtual machines to block unauthorized network access. This helps to prevent malicious actors from accessing your virtual machines from the internet.
- Avoid Downloading Software from Untrusted Sources: Only download software from reputable sources to minimize the risk of installing malware on your virtual machines.
- Implement Antivirus Protection: Install and regularly update antivirus software on your virtual machines to detect and remove malware. This provides an additional layer of protection against malicious threats.
- Back Up Your Data Regularly: Regularly back up your virtual machine data to a separate location. This ensures you can restore your data in case of a security breach or data loss.
Security Considerations for Specific Use Cases
Depending on the specific use cases for your virtual machines, additional security measures might be necessary. For example:
- Sensitive Data Handling: If you’re running virtual machines for handling sensitive data, consider implementing encryption solutions to protect the data at rest and in transit. This helps to prevent unauthorized access even if the virtual machine is compromised.
- Network Security: If your virtual machines are connected to a network, ensure that you implement appropriate network security measures, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems, to protect against network attacks.
Comparison with Alternatives
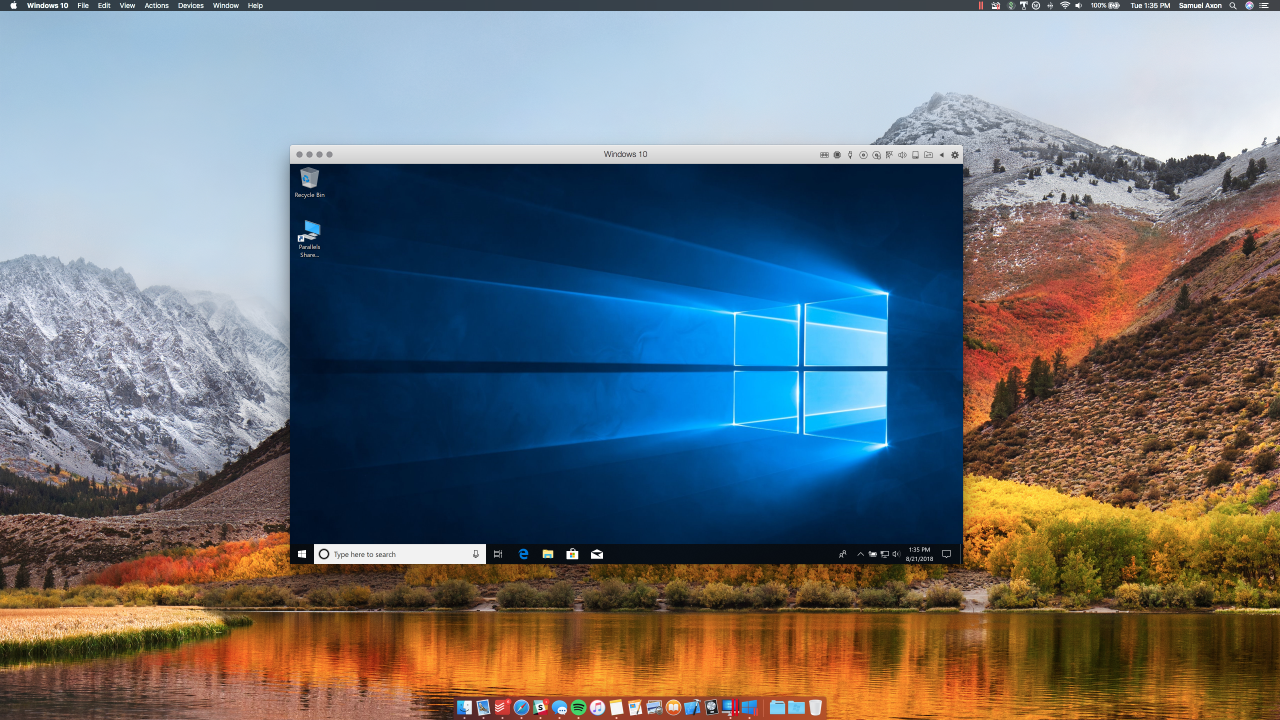
Parallel Desktop is not the only virtualization software available in the market. Several other options offer similar functionality, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Comparing these alternatives helps users choose the best virtualization solution based on their specific needs.
Comparing Parallel Desktop with Other Virtualization Software
This section explores the key differences between Parallel Desktop and its competitors, focusing on price, features, and performance.
- VMware Fusion: VMware Fusion is a popular virtualization solution known for its robust features and compatibility with macOS. While it offers a wider range of features compared to Parallel Desktop, it also comes at a higher price. VMware Fusion’s strengths lie in its enterprise-grade features, excellent performance, and support for various operating systems. However, its higher price point might be a drawback for casual users.
- Oracle VM VirtualBox: Oracle VM VirtualBox is a free and open-source virtualization software. It is highly versatile, supporting various operating systems and offering a wide range of features. However, it might lack the user-friendliness and advanced features found in paid alternatives like Parallel Desktop and VMware Fusion. Oracle VM VirtualBox’s main advantages are its free availability and extensive compatibility, making it a suitable choice for budget-conscious users or those requiring a lightweight solution.
- Microsoft Hyper-V: Microsoft Hyper-V is a virtualization platform integrated into Windows operating systems. It offers excellent performance and seamless integration with Windows environments. However, it is only available for Windows users and lacks the cross-platform compatibility offered by other solutions like Parallel Desktop. Microsoft Hyper-V’s strengths lie in its performance and integration with Windows, making it a suitable choice for Windows users seeking a robust virtualization solution.
Choosing the Right Virtualization Solution
The choice of virtualization software depends on several factors, including the user’s budget, operating system, desired features, and performance requirements.
- Budget: For budget-conscious users, Oracle VM VirtualBox is a free and capable option. However, users seeking advanced features and better performance might consider paid solutions like Parallel Desktop or VMware Fusion.
- Operating System: Parallel Desktop and VMware Fusion are ideal for macOS users, while Microsoft Hyper-V is specifically designed for Windows users. Oracle VM VirtualBox offers cross-platform compatibility, supporting both Windows and macOS.
- Features: Users requiring advanced features like seamless integration with macOS, enhanced performance, and support for various operating systems might prefer Parallel Desktop or VMware Fusion. Oracle VM VirtualBox provides a basic set of features, while Microsoft Hyper-V offers a more robust set within the Windows ecosystem.
- Performance: Parallel Desktop, VMware Fusion, and Microsoft Hyper-V generally offer better performance compared to Oracle VM VirtualBox, especially for resource-intensive tasks. However, Oracle VM VirtualBox can be sufficient for basic virtualization needs.
Wrap-Up
Parallel Desktop empowers users with unparalleled flexibility and efficiency by bridging the gap between operating systems. Whether you’re a professional seeking to run specialized software, a gamer craving access to exclusive titles, or simply someone who enjoys the benefits of multiple operating systems, Parallel Desktop provides a seamless and secure way to enhance your computing journey.
Parallel Desktop is a fantastic tool for running Windows applications on your Mac, but what if you want to create engaging animated characters? You can explore the world of animation with Adobe Character Animator , which allows you to bring your characters to life using your webcam and a few simple controls.
Once you’ve mastered the art of animation, you can even integrate your creations into your Windows applications running smoothly on Parallel Desktop.
