Voice recognition, the ability of computers to understand and interpret human speech, has revolutionized the way we interact with technology. From its humble beginnings in the 1950s, this technology has steadily evolved, becoming an integral part of our daily lives.
Table of Contents
The journey of voice recognition is marked by significant advancements, from early research focused on limited vocabulary systems to sophisticated algorithms powered by machine learning and artificial intelligence. Today, voice recognition is seamlessly integrated into smartphones, smart speakers, and countless other devices, transforming the way we access information, control our environment, and communicate with the world.
History of Voice Recognition
Voice recognition technology has come a long way, evolving from early research efforts to the sophisticated systems we use today. This journey has been marked by significant advancements and breakthroughs that have made voice recognition an integral part of our daily lives.
Early Voice Recognition Systems
The origins of voice recognition can be traced back to the mid-20th century, with initial research focusing on basic speech recognition tasks. Early systems were limited in their capabilities and often struggled with accuracy and robustness. For example, the “Audrey” system developed by Bell Labs in the 1950s could only recognize digits spoken by a single speaker. These early systems relied on simple pattern matching techniques and lacked the computational power and sophisticated algorithms required for more complex speech recognition.
Key Advancements in Voice Recognition
Several key advancements have paved the way for the widespread adoption of voice recognition technology. These include:
- Development of Hidden Markov Models (HMMs): HMMs revolutionized speech recognition by providing a statistical framework for modeling speech patterns. They allowed for the representation of speech as a sequence of states, making it possible to recognize speech even in the presence of noise and variations in speaker characteristics.
- Advancements in Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs): ANNs, inspired by the structure of the human brain, have significantly improved the accuracy and robustness of voice recognition systems. Deep learning, a type of ANN, has enabled the development of highly accurate speech recognition models that can handle complex language variations and background noise.
- Increased Computing Power: The availability of powerful computers and specialized hardware, such as GPUs, has made it possible to train and run complex speech recognition models in real-time. This has enabled the development of practical applications that can handle large amounts of data and process speech quickly.
- Growth of Data Sets: The availability of massive speech data sets has been crucial for training highly accurate speech recognition models. These data sets, often collected from online sources or through crowdsourcing, provide a rich source of information for learning the nuances of human speech.
How Voice Recognition Works
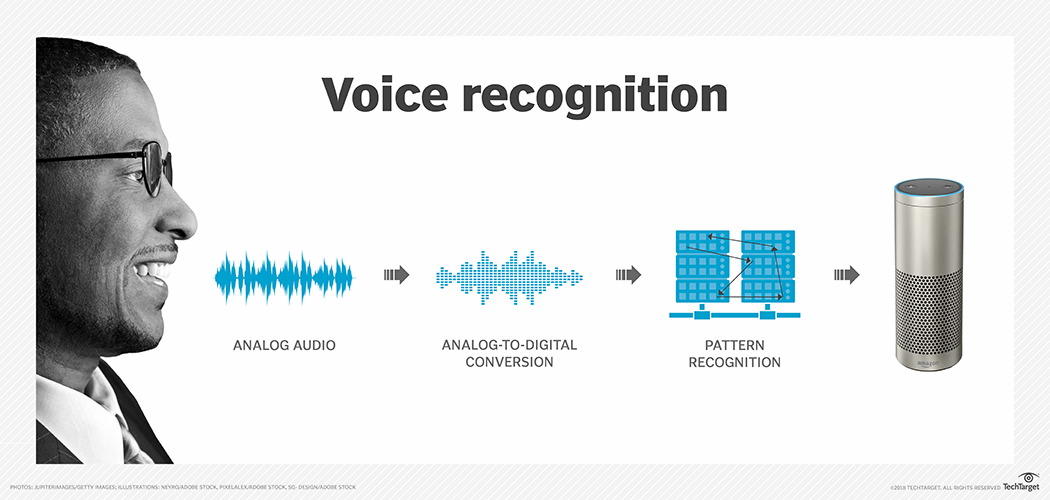
Voice recognition, also known as speech recognition, is a fascinating technology that allows computers to understand and interpret human speech. This technology has become increasingly ubiquitous in our daily lives, powering applications such as virtual assistants, dictation software, and voice search. At its core, voice recognition involves a complex interplay of acoustic analysis, feature extraction, and pattern matching.
Acoustic Analysis
Acoustic analysis is the initial stage of voice recognition, where the raw audio signal is processed to extract meaningful information. The process involves breaking down the speech signal into smaller units, such as phonemes, which are the basic building blocks of spoken language. These phonemes are then analyzed to identify their unique acoustic characteristics, such as frequency, amplitude, and duration.
Feature Extraction
Feature extraction involves converting the raw acoustic data into a set of features that are more suitable for machine learning algorithms. These features are designed to capture the essential characteristics of the speech signal while discarding irrelevant information. Common features include Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCCs), which represent the spectral envelope of the speech signal, and delta coefficients, which capture the rate of change in the spectral envelope over time.
Pattern Matching
Pattern matching is the final stage of voice recognition, where the extracted features are compared to a database of known speech patterns. This process involves using statistical models or machine learning algorithms to determine the most likely word or phrase that corresponds to the input speech signal.
Acoustic Models
Acoustic models are statistical models that map acoustic features to phonetic units. They are trained on large datasets of speech data, where each utterance is labeled with its corresponding phonetic transcription. Acoustic models are crucial for converting the raw acoustic signal into a sequence of phonetic units, which can then be used by language models to generate text.
Language Models
Language models are statistical models that predict the likelihood of a sequence of words. They are trained on large text corpora and capture the grammatical and semantic relationships between words. Language models are used in voice recognition systems to improve the accuracy of the recognized text by incorporating contextual information.
Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
Machine learning and artificial intelligence play a critical role in voice recognition systems. Machine learning algorithms are used to train acoustic models and language models, while artificial intelligence techniques are employed to improve the accuracy and robustness of the systems. For example, deep learning algorithms have been successfully used to develop highly accurate acoustic models, while natural language processing techniques are used to improve the understanding of context and intent in speech recognition systems.
Applications of Voice Recognition
Voice recognition technology has revolutionized how we interact with computers and devices, offering a more intuitive and efficient way to communicate. This technology is widely used across various industries, empowering individuals and businesses alike to streamline tasks, enhance productivity, and improve accessibility.
Voice Recognition Applications Across Industries
Voice recognition technology has a wide range of applications across different industries, transforming the way businesses operate and individuals interact with technology.
| Industry | Application | Example | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Service | Interactive Voice Response (IVR) Systems | Automated customer service systems that use voice recognition to understand customer queries and provide relevant information or solutions. | Reduced wait times, improved customer satisfaction, and cost savings. |
| Healthcare | Medical Transcription | Doctors and nurses can dictate patient notes and medical reports, which are automatically transcribed into text. | Increased efficiency, reduced errors, and improved documentation accuracy. |
| Education | Speech-to-Text Software | Students with learning disabilities can use voice recognition software to convert spoken words into text, making it easier to take notes and participate in class. | Improved accessibility for students with disabilities, enhanced learning experience, and increased productivity. |
| Finance | Fraud Detection | Voice recognition can be used to authenticate users and detect fraudulent activity, such as unauthorized access to accounts. | Enhanced security, reduced risk of fraud, and improved customer trust. |
| Automotive | Voice-Activated Navigation and Control | Drivers can use voice commands to control navigation, music playback, and other vehicle functions without taking their hands off the steering wheel. | Improved safety, enhanced convenience, and a more engaging driving experience. |
| Retail | Virtual Assistants | Retailers can use voice-activated virtual assistants to provide customer support, answer questions, and guide shoppers through the store. | Personalized shopping experience, improved customer satisfaction, and increased sales. |
| Manufacturing | Voice-Controlled Robots | Voice recognition technology enables workers to control robots using voice commands, improving efficiency and reducing the risk of accidents. | Increased productivity, improved safety, and reduced labor costs. |
| Legal | Legal Transcription | Lawyers can use voice recognition software to transcribe legal documents, such as depositions and court proceedings. | Increased efficiency, reduced errors, and improved accuracy in legal documentation. |
Impact on User Experience and Accessibility
Voice recognition technology has significantly impacted user experience and accessibility across various devices and platforms.
- Enhanced User Experience: Voice recognition offers a more natural and intuitive way to interact with devices, eliminating the need for physical keyboards or touchscreens. This allows users to perform tasks quickly and efficiently, improving overall user satisfaction.
- Increased Accessibility: Voice recognition technology empowers individuals with disabilities, such as visual impairments or motor difficulties, to interact with technology more easily. For example, screen readers use voice recognition to read text aloud, making it accessible to visually impaired users.
- Improved Accessibility for Diverse Users: Voice recognition technology is also beneficial for individuals who speak different languages or have accents. It can be trained to recognize a wide range of accents and dialects, making it more accessible to a wider audience.
Voice Recognition in Devices
Voice recognition technology has become ubiquitous, seamlessly integrated into our daily lives through a wide range of devices. From smartphones and smart speakers to automotive systems and home appliances, voice recognition has revolutionized the way we interact with technology.
Voice Recognition in Smartphones
Smartphones have become the primary platform for voice recognition, enabling users to perform various tasks through voice commands.
- Virtual Assistants: Smartphones are equipped with virtual assistants like Siri, Google Assistant, and Alexa, which allow users to make calls, send messages, set reminders, and control other device functions using voice commands.
- Voice Search: Voice search allows users to find information online by speaking their queries instead of typing them. This feature is particularly useful for hands-free searches and for users with limited mobility.
- Voice Dictation: Voice dictation enables users to create text documents, emails, and messages by speaking instead of typing. This feature enhances productivity and convenience for users who prefer voice input.
Voice Recognition in Smart Speakers
Smart speakers, such as Amazon Echo and Google Home, are dedicated devices that primarily rely on voice recognition for user interaction.
- Music Playback: Smart speakers allow users to control music playback, including selecting songs, adjusting volume, and switching between music services, using voice commands.
- Home Automation: Voice recognition enables users to control smart home devices, such as lights, thermostats, and appliances, through voice commands. This feature provides convenience and enhanced control over home environments.
- Information Retrieval: Smart speakers can access information from the internet, providing weather updates, news headlines, and other relevant data based on voice queries.
Voice Recognition in Other Devices
Voice recognition is also integrated into a wide range of other devices, including:
- Automotive Systems: In-car systems like Apple CarPlay and Android Auto utilize voice recognition for hands-free navigation, phone calls, and music playback, enhancing safety and convenience while driving.
- Home Appliances: Smart refrigerators, washing machines, and ovens incorporate voice recognition to allow users to control appliance settings, monitor progress, and receive alerts using voice commands.
- Wearable Devices: Smartwatches and fitness trackers utilize voice recognition for controlling music playback, receiving notifications, and setting reminders, providing hands-free access to information and functions.
Comparison of Voice Recognition Capabilities
Different devices and platforms exhibit varying levels of accuracy and functionality in voice recognition.
- Accuracy: The accuracy of voice recognition systems varies depending on factors such as the quality of the microphone, the processing power of the device, and the complexity of the language model used.
- Language Support: The number of languages supported by voice recognition systems varies. Some systems offer support for multiple languages, while others may be limited to a specific language.
- Customization: Voice recognition systems can be customized to adapt to individual user voices and accents, improving accuracy and personalization.
Challenges and Opportunities of Voice Recognition in Embedded Systems
Voice recognition in embedded systems presents unique challenges and opportunities.
- Limited Resources: Embedded systems often have limited processing power, memory, and battery life, which can pose challenges for running complex voice recognition algorithms.
- Noise and Interference: Embedded devices are often exposed to noisy environments, which can interfere with voice recognition accuracy.
- Security Concerns: Voice recognition systems can be vulnerable to spoofing attacks, where unauthorized individuals can impersonate legitimate users.
Voice Recognition for Security
Voice recognition has emerged as a powerful tool for enhancing security in various applications, leveraging its ability to authenticate individuals based on their unique vocal patterns. This technology is increasingly being integrated into systems that require robust security measures, providing an additional layer of protection against unauthorized access.
Voice Recognition for Authentication
Voice recognition can be used for authentication by comparing a user’s voice against a stored template or profile. This process involves analyzing various vocal characteristics, such as pitch, intonation, and rhythm, to verify the user’s identity. The authentication process typically involves the following steps:
- Enrollment: During the initial setup, the user records a series of voice samples, which are used to create a unique voice profile. This profile is then stored securely in a database.
- Verification: When the user attempts to access a system or service, they are prompted to speak a specific phrase or answer a question. Their voice is then analyzed and compared to the stored profile.
- Authentication: If the voice matches the stored profile, the user is authenticated and granted access. If there is a mismatch, access is denied.
Security Implications of Voice Recognition
While voice recognition offers a promising security solution, it’s crucial to understand its potential vulnerabilities and countermeasures.
- Spoofing Attacks: One of the primary concerns is the possibility of spoofing attacks, where an attacker attempts to impersonate a legitimate user by mimicking their voice. This can be achieved through techniques like replay attacks, where a recording of the user’s voice is played back to the system, or synthetic voice generation, where artificial intelligence (AI) is used to create a convincing imitation.
- Voice Mimicry: Advanced AI algorithms are becoming increasingly sophisticated, making it possible to create highly realistic voice mimics. This poses a significant challenge to voice recognition systems, as it can be difficult to distinguish between a real voice and a synthetic one.
- Privacy Concerns: Voice recognition systems collect and store voice data, raising concerns about privacy. This data could be potentially used for unauthorized purposes or compromised by malicious actors.
To mitigate these vulnerabilities, several countermeasures can be implemented:
- Multi-Factor Authentication: Combining voice recognition with other authentication methods, such as passwords or biometrics, can strengthen security by requiring multiple forms of verification.
- Live Voice Detection: Incorporating live voice detection techniques can help distinguish between live voices and recordings, making it more difficult for attackers to carry out replay attacks.
- Voice Variability Analysis: Analyzing variations in voice patterns over time can help detect spoofing attempts. For example, if an attacker tries to use a recording of a user’s voice, the system may notice inconsistencies in the voice pattern compared to the stored profile.
- Secure Data Storage and Encryption: Implementing robust data storage and encryption measures can help protect voice data from unauthorized access and breaches.
Real-World Applications of Voice Recognition for Security
Voice recognition is being increasingly used for security purposes in various real-world applications:
- Access Control: Voice recognition is used to grant access to secure areas, such as buildings, offices, and data centers. For instance, a voice recognition system can be integrated with door locks or security gates to allow authorized personnel to enter by simply speaking a designated phrase.
- Mobile Device Security: Voice recognition is becoming a common feature on smartphones and tablets, allowing users to unlock their devices using their voice. This provides an alternative to traditional PIN codes or fingerprint scanners.
- Financial Transactions: Some banks and financial institutions are adopting voice recognition for secure online transactions, allowing users to authenticate themselves through voice verification.
- Call Center Authentication: Voice recognition can be used to verify the identity of callers in call centers, ensuring that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive information.
Voice Recognition and Natural Language Processing
Voice recognition and natural language processing (NLP) are intertwined technologies that work together to enable computers to understand and respond to human speech. While voice recognition focuses on converting spoken words into text, NLP takes this text further by analyzing its meaning, structure, and context.
NLP techniques are essential for improving the accuracy and understanding of voice recognition systems. By analyzing the grammatical structure, semantics, and intent of spoken language, NLP helps to overcome the limitations of simple word-by-word transcription.
NLP Techniques for Enhanced Voice Recognition
NLP techniques play a crucial role in enhancing the accuracy and understanding of voice recognition systems by addressing the inherent complexities of natural language. These techniques enable the system to go beyond simple word recognition and delve into the meaning and intent behind spoken words.
- Part-of-Speech Tagging: NLP techniques like part-of-speech tagging help identify the grammatical function of each word in a sentence. For example, recognizing “play” as a verb in “Play the song” allows the system to understand the intended action.
- Named Entity Recognition: This technique identifies and categorizes entities such as people, places, and organizations within text. In the sentence “I need to book a flight to London,” named entity recognition helps identify “London” as a location, facilitating accurate understanding of the user’s request.
- Sentiment Analysis: NLP enables the system to analyze the emotional tone of spoken language, helping to interpret the user’s intent. For example, in the sentence “This music is terrible,” sentiment analysis identifies the negative sentiment, enabling the system to adjust its response accordingly.
- Semantic Analysis: NLP techniques analyze the meaning of words and phrases in context, allowing the system to understand the user’s intent beyond literal interpretation. For instance, “What’s the weather like today?” and “Is it raining?” both convey the same intent despite different wording.
Challenges of Processing Natural Language in Voice Recognition Systems
Despite advancements in NLP, processing natural language in voice recognition systems remains challenging due to the inherent complexities of human speech.
Voice recognition technology has come a long way, enabling us to control devices and software with our voices. This technology can also be applied to music editing, making it easier to manipulate audio tracks without needing to use a mouse or keyboard.
If you’re looking for a powerful and intuitive tool for music editing, check out this music editor which utilizes voice recognition to enhance the user experience. The future of voice recognition is exciting, with potential applications extending far beyond music editing.
- Ambiguity: Natural language is often ambiguous, with words having multiple meanings depending on context. For example, “bank” can refer to a financial institution or the edge of a river. NLP algorithms need to resolve such ambiguities to understand the user’s intent accurately.
- Dialects and Accents: Different dialects and accents can significantly alter the pronunciation of words, posing challenges for voice recognition systems. NLP techniques are used to identify and adapt to variations in speech patterns, improving the system’s accuracy across diverse user populations.
- Slang and Idioms: Informal language, slang, and idioms present unique challenges for NLP. These expressions often deviate from standard grammatical rules and require specialized techniques for interpretation.
- Background Noise: Real-world environments are often noisy, introducing interference that can distort speech signals. NLP techniques are used to filter out noise and enhance the clarity of speech, improving the accuracy of voice recognition.
Ethical Considerations of Voice Recognition
Voice recognition technology, while offering convenience and accessibility, raises significant ethical concerns that must be addressed to ensure responsible development and deployment. These concerns encompass privacy violations, potential biases in the technology, and the misuse of voice recognition for surveillance and profiling.
Privacy Concerns
Voice recognition technology inherently involves the collection and analysis of sensitive personal data, namely voice recordings. This raises serious privacy concerns, as individuals may not be aware of the extent to which their voice data is being collected, stored, and analyzed.
- Uninformed Consent: Individuals may not be fully informed about the implications of using voice recognition systems, particularly regarding the collection and use of their voice data.
- Data Retention and Sharing: Concerns exist about the duration for which voice data is retained and whether it is shared with third parties, especially without explicit consent.
- Unauthorized Access: The potential for unauthorized access to voice data raises concerns about identity theft, financial fraud, and other security breaches.
Bias in Voice Recognition
Voice recognition systems are trained on large datasets of voice recordings, which can reflect existing societal biases. This can lead to inaccurate or discriminatory outcomes for individuals with certain accents, dialects, or speech patterns.
- Accuracy Disparities: Voice recognition systems often exhibit lower accuracy for individuals with accents or dialects that are underrepresented in the training data.
- Amplification of Social Biases: If training data reflects existing biases, the resulting voice recognition systems may perpetuate these biases, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes.
- Limited Representation: The lack of diverse voices in training data can result in systems that are less accurate and reliable for individuals from marginalized groups.
Surveillance and Profiling
The increasing use of voice recognition technology raises concerns about its potential for surveillance and profiling. Voice recordings can be used to identify individuals, track their movements, and infer their personal preferences and behaviors.
- Surveillance in Public Spaces: The deployment of voice recognition systems in public spaces, such as shopping malls or airports, raises concerns about mass surveillance and privacy violations.
- Profiling and Discrimination: Voice data can be used to create profiles of individuals, potentially leading to discrimination in areas like employment, insurance, or access to services.
- Government and Law Enforcement Use: The use of voice recognition by government agencies and law enforcement raises concerns about potential misuse for political repression or targeting individuals based on their speech patterns.
Regulation and Guidelines
To mitigate the ethical risks associated with voice recognition technology, it is crucial to establish clear regulations and guidelines for its development, deployment, and use.
- Data Privacy and Security: Regulations should address data collection, storage, and sharing practices, ensuring that voice data is handled responsibly and securely.
- Transparency and Informed Consent: Individuals should be fully informed about how their voice data is being used and have the right to consent or opt out of data collection.
- Bias Mitigation: Guidelines should be developed to address bias in voice recognition systems, including the use of diverse training data and ongoing monitoring for fairness and accuracy.
Future of Voice Recognition

Voice recognition technology has come a long way, but it’s only scratching the surface of its potential. As we move forward, we can expect even more remarkable advancements in this field, driven by innovations in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and other emerging technologies.
Advancements in Accuracy and Robustness
Voice recognition systems are becoming increasingly sophisticated, thanks to the rapid progress in AI and machine learning. These advancements are enabling systems to better understand and interpret human speech, even in challenging environments with background noise or accents.
- Improved Acoustic Modeling: Researchers are developing more accurate acoustic models that can effectively filter out noise and identify subtle variations in speech patterns. This will enhance the system’s ability to recognize speech in noisy environments and handle different accents.
- Enhanced Language Understanding: Advancements in natural language processing (NLP) are enabling voice recognition systems to understand the context and meaning of spoken words more effectively. This will allow for more natural and intuitive interactions, even in complex conversations.
- Adaptive Learning: Voice recognition systems are becoming more adaptive, capable of learning from user interactions and adjusting their models accordingly. This will enable them to personalize their responses and improve their performance over time.
Versatility and Integration
The future of voice recognition lies in its versatility and seamless integration into various aspects of our lives. Voice recognition will become a ubiquitous interface, empowering us to interact with technology in new and innovative ways.
- Multimodal Interactions: Voice recognition will be combined with other input methods, such as gestures, facial expressions, and even brain-computer interfaces, to create more intuitive and engaging user experiences. This will lead to more natural and seamless interactions with technology.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Integration: Voice recognition will become an integral part of the IoT, enabling us to control smart home devices, appliances, and other connected systems using voice commands. This will simplify our lives and make our homes more intelligent and responsive.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR): Voice recognition will play a crucial role in VR/AR experiences, providing a more immersive and interactive way to control virtual environments and interact with digital objects.
Impact of Emerging Technologies
The convergence of voice recognition with other emerging technologies, such as AI and the IoT, will lead to a transformative shift in how we interact with the world around us.
- AI-Powered Voice Assistants: AI will play a crucial role in enhancing the capabilities of voice assistants, enabling them to understand complex requests, learn from user preferences, and provide more personalized and proactive assistance.
- Smart Homes and Cities: Voice recognition will be essential for creating intelligent homes and cities that respond to our needs and preferences. Imagine controlling your home’s lighting, temperature, and security systems with your voice, or using voice commands to navigate public transportation and access information in real-time.
- Healthcare and Education: Voice recognition will revolutionize healthcare and education, enabling more personalized and efficient delivery of services. Imagine using voice commands to access medical records, schedule appointments, or receive personalized health advice. In education, voice recognition can be used to create interactive learning environments, provide real-time feedback, and personalize the learning experience.
Voice Recognition in Specific Industries

Voice recognition is rapidly transforming various industries, revolutionizing how businesses operate and interact with customers. One industry significantly impacted by voice recognition technology is healthcare.
Voice Recognition in Healthcare
Voice recognition technology is being implemented in healthcare to improve efficiency, accuracy, and patient care. Voice recognition software allows medical professionals to dictate patient notes, medical reports, and prescriptions, eliminating the need for manual transcription.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Voice recognition software can be integrated with EHR systems, enabling physicians to directly input patient information, diagnoses, and treatment plans through voice commands. This streamlines the documentation process, saving time and reducing errors.
- Medical Imaging: Voice recognition can assist radiologists in interpreting medical images. By using voice commands, radiologists can quickly annotate images, create reports, and dictate findings, improving efficiency and accuracy.
- Telemedicine: Voice recognition technology plays a crucial role in telemedicine, allowing doctors to remotely diagnose and treat patients. Patients can use voice commands to describe their symptoms and receive virtual consultations, enhancing access to healthcare.
Despite its benefits, voice recognition in healthcare faces challenges. Ensuring the accuracy and security of voice data is paramount. The technology needs to be robust enough to handle medical jargon and different accents. Moreover, regulations surrounding patient privacy and data security must be addressed.
The future of voice recognition in healthcare is promising. Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and natural language processing (NLP) are enabling more sophisticated voice recognition systems that can understand complex medical terminology and provide personalized insights. Voice-activated assistants are being developed to help patients manage their health, track medications, and communicate with healthcare providers.
Final Thoughts
Voice recognition has come a long way, and its future looks even brighter. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect voice recognition to become even more accurate, robust, and versatile, further blurring the lines between humans and machines. With its potential to revolutionize various industries and enhance our lives in countless ways, voice recognition is poised to play a central role in shaping the future of technology and human interaction.
